How Virtual Reality Improves the Standards of Medical Education and Training
Medical Virtual Reality offers excellent opportunities for healthcare providers, practitioners, researchers, residents, patients, and chemists. Here’s a brief overview.
Virtual Reality: Increasing success rate and establishing trust in medical education
In 2013, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated a shortage of approximately 7.2 million health care professionals worldwide. The report also stated that this shortage is expected to reach 12.9 million by 2035. Besides the deficiency and disproportionate distribution of healthcare workers, the inadequacy of training programs also affects the delivery of uniform healthcare services worldwide. Leading healthcare organizations have been focusing on developing strategies that can increase the number of healthcare workers and enhance the quality and relevance of medical training.
In recent years, several modes of eLearning have been used to disseminate information and impart training to medical students, out of which Virtual Reality Applications deserve a special mention. Virtual Reality Environments (VREs) allow users to experience real-life scenarios via simulated counterparts and gain practical knowledge that would otherwise be difficult to comprehend in a real environment.
Read more: Is Mixed Reality the Future of the Healthcare Industry?

Here are a few examples of how VR improves medical education standards and how it enables novice medical personnel to learn concepts in environments that replicate real-life scenarios.
1. Reduce stress and anxiety among medical students
Medical and traumatic emergencies can be daunting and stressful, especially for the early-career medical personnel. Preparing novice doctors to respond effectively to medical emergencies before being confronted with a real scenario is challenging. Unnatural or high-cost training modalities fail to replicate the stress and gravity of real-world trauma management realistically. Immersive virtual reality (IVR) may provide a unique training solution.
VR-based medical training recipients report better learning of anatomical positions, reduction in surgery time in the real environment, increase in the safety of both physician and patient, positive psychological effects on learners, reduction in training costs and efforts, and overall improvement. 68% of nursing and 58% of medical interns reported that VR-based training has significantly reduced their anxiety about occupational needlestick or sharp injuries (NSI) prevention.
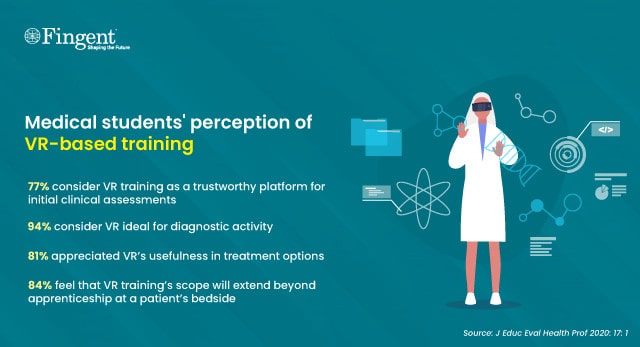
2. Ensure uninterrupted in-hospital training
During April-July 2020, when most countries went to stringent lockdown measures to curb the spread of the coronavirus, several medical colleges and universities adopted virtual reality to supplement the traditional in-hospital medical training. Due to in-hospital access bans, the training providers offered students virtual patient-based training, debriefing, and simulated clinical scenarios on a case-by-case basis, all via virtual reality environments.
A recent report on students’ perception of VR-based medical training found that:
- 77% of medical students considered VR training to be a trustworthy platform for initial clinical assessments
- 94% remarked that VR is ideal for diagnostic activity, and 81% appreciated its usefulness in treatment options
- Furthermore, 84% of students felt that the scope of VR training would move beyond apprenticeship at a patient’s bedside

3. Immersive VR environments help develop empathy
The most significant advantage of virtual reality is that it allows users to experience any situation from any perspective. In that way, it can be called the “ultimate empathy machine.” Patients suffering from traumas such as memory loss, physical or mental abuse, age-related health issues, Alzheimer’s disease, drug addiction, and other ordeals need a soothing atmosphere and reassuring words to recover quickly. Immersive VR training is an effective teaching method to help medical students develop empathy towards such patients.
An educational project conducted by the University of New England (UNE) successfully used VR to teach empathy to medical and health profession students. The project used a VR tool called “Alfred Lab app” – to teach students about macular degeneration and hearing loss from a 74-year-old African American man’s perspective. Realizing an aged and ailing patient’s thoughts and concerns enables the residents to develop empathy towards such patients.
4. Improve practitioners’ skills, speed, and mobility in operating rooms
From rote memorization of theories, the modern medical training practice has evolved to imparting skills in life-like environments using virtual reality simulations. Even in the absence of faculty, VR systems enable students to learn practical surgical concepts when faced with a given patient. VR systems make medical training access more broad-based and flexible. Medical professionals can use VR to visualize the human body’s interior and learn better about human anatomy.
According to a study published by the Journal of Advances in Medical Education & Professionalism, the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) has proclaimed that residents need to be trained by simulation tools before attempting any patient interventions in real life. The board also finds immersive VR training to be effective in mechanical ventilation and invasive hemodynamic monitoring.
Dr. Dimitris Stefanidis, professor and research scholar at Indiana University School of Medicine, concluded in a study that surgical residents who underwent training in laparoscopic suture using video simulators had reported improved operative performance, speed, and mobility at the end of the practice. Performing surgeries that require vast experience and sensitivity, such as an osteotomy (bone-cut surgery), can be simplified for surgeons through virtual simulations. Immersive simulations along with tactical feedback are safer and cost-effective than traditional teaching methods.
5. Impart health education and awareness among patients
In addition to practitioners, patients also can gain awareness of their medical conditions and treatment principles using VR. Clinical professionals can use simulated environments to communicate the impact of unpleasant lifestyle practices such as noxious drug usage, metabolic dysfunctions, obesity, growth of certain tumors, the effect of smoking and drinking on lung and liver functions, etc.
Chronically ailing and hospitalized patients can use VR goggles or headsets to experience their home in an immersive environment and chat with their family members. By installing a 360-degree camera in their home, the patient’s family can make sure that the patient experiences the interaction just like how he/she used to feel it while at home. During the COVID-19 pandemic, VR was highly applied in remote sites to facilitate telemedicine, control the spread of infection, plan, treat, and provide proper awareness to people regarding this disease.
Read more: The Application and Impact of Information Technology in Healthcare
Getting started with VR
Medical VR is no more a sci-fiction. VR-trained surgeons report a 230% boost in their overall performance compared to their traditionally-trained counterparts.
VR can help you conduct engaging medical conferences, help women get through labor pain, train surgeons and medical residents, reduce pain and anxiety among patients, and expedite recovery in physical therapy by tailoring exercises to patients’ therapeutic needs.
If your next question is how to start with VR, Fingent helps you develop these virtual simulators:
- ACLS (Advanced Cardiac Life Support System)
- Accident Trauma Care Standard Operating Procedures
- Orthopedic or Cardiac surgical procedure that involves using complex tools
- Neo-Natal Resuscitation Simulator (GOLDEN MINUTE PROTOCOL)
Would you like to discuss that with our expert? Drop us a line, and a member of our team will get back to you shortly.
Stay up to date on what's new

Recommended Posts

24 Oct 2023 Retail B2B
Explore Innovative Business Possibilities with Smart Retail Technologies
Our digital era is a whirlwind of change, with technology driving transformation at breakneck speed. It's not just about adopting new gadgets; it's about recognizing technology's influence on consumer interactions.……
04 Aug 2023 B2B
Augmented Reality: Taking Product Demos To A Whole New Level!
In the fast-paced world of business, where attention spans are shrinking and competition is fierce, a successful product launch can make all the difference. You've invested countless hours refining your……

08 Jul 2023 B2B
AR, VR, and 3D Configurators for Real Estate
The implementation and development of immersive digital technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Augmented Reality, Virtual Reality, Machine Learning, and 3D Configurators have drastically changed the way the world works. These……
23 Feb 2023 Real Estate B2B
Futuristic Technologies Transforming The Real Estate Industry!
According to a 2020 report, 58% of real estate brokers have a clearly defined digital strategy, a figure that represents a 6% increase from the two previous years and thus……
Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new











