Types of Application Software: Guide for 2025
Table of Contents
- Licensing & Monetization of Application Software
- How to Choose The Right Application Software For Your Business
- Key Trends Shaping Application Software Development in 2025
- Cost of Developing an Application Software for Your Business
- FAQ
- Top Emerging Technologies in Application Software
- Develop Your Application Software With Fingent
Application software offers a plethora of options tailored to meet the diverse needs and objectives of users and businesses. Today, AI is a major force in application software. AI-integrated applications are the hot cakes now; they significantly enhance efficiency, speed, and productivity. Choosing the right application software can transform operations and profoundly influence your bottom line, positively impacting business outcomes.
Deep dive into everything you need to know about application software and how to choose the right type of application software for your business.
Understanding Application Software: Types and Business Benefits
What is application software?
Application software offers a plethora of options tailored to meet the diverse needs and objectives of users and businesses. Today, AI is a major force in application software. AI-integrated applications are the hot cakes now; they significantly enhance efficiency, speed, and productivity. Choosing the right application software can transform operations and profoundly influence your bottom line, positively impacting business outcomes.
The application software has evolved remarkably, and it consists of AI capabilities, cloud-native architecture, and cross-platform compatibility. Companies today are making use of different intelligent applications to simplify their activities, improve customer experiences, and boost strategic plans.
Examples of application software
Today, we have many high-end application software that define how we live and accommodate our ever-evolving requirements. Widely used application software includes office productivity tools, business applications, project management tools, creative tools, communication tools, and many more.

Microsoft Office 365
(Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, Copilot)

Google Workspace
(Docs, Sheets, Slides, Gmail)

Infince
(Enterprise Application Cloud)

Salesforce CRM

Oracle NetSuite

Zoho CRM

SAP S/4HANA Cloud
Microsoft Dynamics 365

Asana

Trello

ClickUp

Monday.com

Adobe Creative
Cloud Applications
Figma

Canva

CorelDraw

AutoCAD

Slack

Microsoft Teams

Infince

Zoom


Wynk
MX Player

VLC Media Player

Spotify

Pandora
What is the difference between system software and application software?
Software can be categorized into two categories: System Software and Application Software. System software is used to manage the main functions of the computer and hardware devices, and application programs enable users to accomplish certain tasks such as writing documents, sending emails, or even managing data.
They both differ significantly when it comes to design and purpose.
Application Software
- Application software is designed to accomplish tasks for a specific purpose based on user requests.
- Application software is third-party software that can be downloaded and installed according to the user’s needs.
- Application software is commonly referred to as specific-purpose software.
- Hosted on the platform, which is provided by the system software.
- Programmed in high-level languages, such as C++, Python, or JavaScript.
- Application software cannot run independently and needs the presence of system software.
- Programming of applications is comparatively simpler.
- Runs in the foreground and performs a task based on user requests.
-
Performs user-specific tasks for which
it is designed. - The user interacts with the application software.
- Application software is not mandatory, and the system can function without it.
- Examples: word processor, web browser, media player, Photoshop, etc.
System Software
- System software is designed to control and manage the hardware and other resources of the system.
-
System software is pre-installed with the operating
system. - System software is commonly referred to as general-purpose software.
- It acts as an interface between application software and the system.
- Developed in a low-level language or machine code that is more compatible with the system hardware.
-
System software can run
independently. - Programming of system software is complex.
-
It acts as a platform and runs in the
background. - Performs primary functions of process management, memory management, task scheduling, hardware installation, etc.
- Users don't interact with system software.
-
System software is mandatory for a system
to function. -
Examples: compiler, assembler, debugger,
driver, etc
Key functions of application software for businesses
Application software programs are designed to execute a wide array of functions. Its primary functions can vary depending on the users' requirements. Depending on the industry or business area, it is possible to develop the application software to fulfill a particular purpose.

Task Automation
Automating routine tasks, such as data entry, sales emails, and marketing emails, saves a lot of manual work and allows employees to perform more strategic tasks.
Data Management
Gather, store, sort, and classify large volumes of information, make informed judgments, and trace patterns.

Communication and Collaboration
Maximizing smooth communication among the employees, partners, and customers, as well as working together on common projects.

Process Optimization
Enhancing organizational workflow and efficiency in different departments, resulting in cost cuts and enhanced productivity.
Innovative and efficient production
Allows the production of high-quality files, presentations, designs, and multimedia output.

Problem Solving
Providing targeted tools to handle specialized business purposes, be it in the field of inventory management, sales forecasting, or data security.
Benefits of application software for businesses
Most organizations invest in buying or building application software to suit their business model. This software comes with innumerable benefits that you can't resist executing the ideal application software in your business/organization.

Enhanced customer service and satisfaction
Application software will be able to couple your CRM with other essential business programs. It delivers better and accurate information about the customers, which makes your customer service faster and more effective. Consequently, it enhances customer service and boosts customer satisfaction.

More power to decision-making
As application software gives you more reliable and updated business information, your decision-making process will be backed by accurate data. It helps you keep track of past performances and decisions, forecast future trends, plan your budgets, improve hiring and retention, and define contingency plans. Hence, well-designed application software is a CEO’s companion in every sense.

Improved productivity
Application software is useful in the automation of tasks so that employees can save time on strategic purposes of the business and produce more quantity of work in a particular time. For e.g., OCR programs that decode scanned images or PDF documents, such as insurance, banking, and law industries, can find these very useful. On the same note, RPA applications can minimize monotonous tasks, including responding to emails, checking claims in relation to a prescribed set of rules or checks, or payroll discrepancies.
Robust data security
You can integrate application software with your existing systems in the most secure way with the help of a reliable custom software development company like Fingent. You get complete control over the third-party systems integrated into your software. The application software resides within your firewall and is upgraded and maintained throughout with the support of a partner.

More flexibility
The fringe benefit of using application software is that it provides the freedom to integrate and gather data from multiple sources in a single place. This reduces your time considerably and provides a hassle-free process to create customized reports, avoiding the use of numerous applications to store data.

Seamless management
Application applications are also best at getting rid of risks, conducting research, classification of tasks as well as offering proper solutions with negligible possibilities of human error. Thus, it can be viewed as an ultimate tool that can offer a smooth experience to organizations as they deal with their business operations at large.
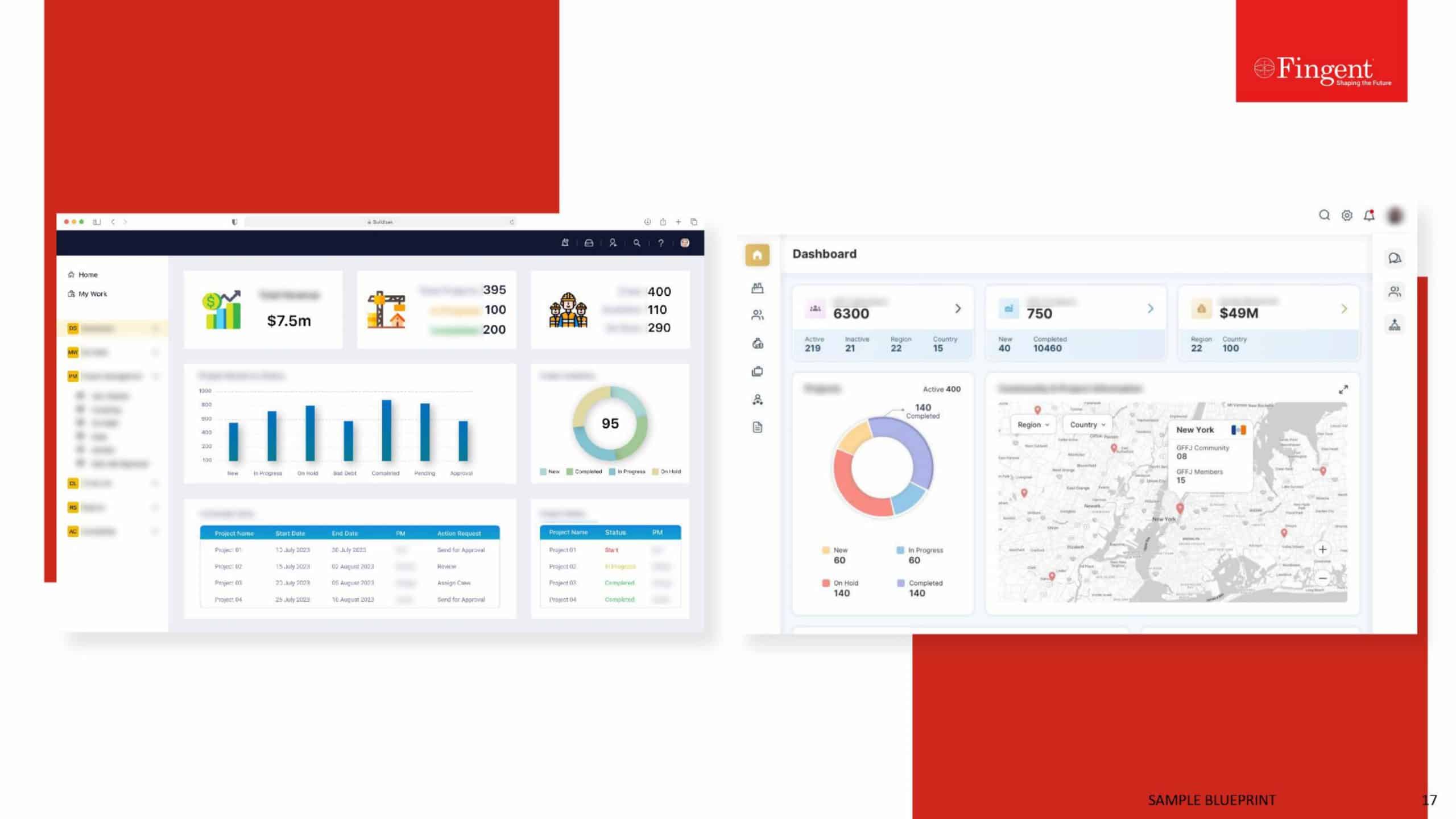
Types of Application Software
Application software can be broadly classified into General Applications, Business Applications, AI-powered Applications, and Custom Applications. Application software is no longer a one-size-fits-all solution. In today’s business landscape, software tools are categorized based on functionality, complexity, and the specific needs they serve. Picking up the right application software for your specific needs improves function and efficiency. The use of the software is rampant across every domain, including banking, healthcare, education, retail, travel, logistics, etc.
General Applications - Everyday Productivity & Collaboration Tools
In present-day companies, general-purpose applications play a crucial role in digital productivity. Such programs assist people and groups in crafting content, handling data, communication, and staying organized. They are usually cloud-based, cross-platform, and are becoming more and more run by embedded AI.

Word Processing Software
To draft, format, and edit text-based reports, proposals, manuals, and other business material. These applications are rich in formatting, collaboration, and version control.
Examples: Google docs, Microsoft word, notion
Spreadsheet Software
Spreadsheets find a lot of applications in organizing and tabulating data, calculations, budgeting, and reporting. They facilitate functions, charts, filters, and conditional formats in order to make data management easy.
Examples: Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, Airtable
Presentation Tools
These tools assist users to author and present slide-based presentations during meetings, pitches and training. They include features such as templates, transitions, and multimedia support.
Examples: Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, Canva
Email & Scheduling
Calendar and e-mail clients are used to coordinate and communicate, as well as organize meetings. They facilitate time-zone conscious scheduling, contact organization, and inbox management.
Examples: Microsoft Outlook, Gmail, Google Calendar, Calendly
Team Collaboration & Messaging
Tools that help teams communicate more efficiently by messaging, group channels, file spaces, and video calls. These tools assist in sustaining continuity and visibility in scattered groups.
Examples: Slack, Microsoft Teams, Zoom
Cloud Storage & File Management
Cloud file storage services enable an enterprise to access, store, and share documents on devices anytime, anywhere. It has features such as versioning of files, rights of folders, and managing backups.
Examples: Google Drive, Infince, Dropbox, Microsoft OneDrive
Business Applications
Business applications are software tools used in businesses to enable, streamline, or support the main processes within an organization. These applications are critical in enhancing scalability, decision-making, and efficiency in terms of handling customer relations and operations of financial processes.

Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
The CRM software assists firms in handling customer and prospect relationships through the sales and service lifespan. It stores customer information, monitors interaction, and provides marketing and sales automations.
Examples: Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
ERP systems have merged more crucial functions of business, like finance, supply chain, procurement, and human resources, under one roof. They give real-time visibility and increase the consistency of data, as well as allow smooth operations within departments.
Examples: SAP S/4HANA, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics 365
Project & Task Management
These tools help teams plan, organize, and follow up on projects and daily activities. It has features such as timelines, the distribution of tasks, progress monitoring, and collaboration to maintain alignment and responsibility.
Examples: Asana, Monday.com, ClickUp, Jira
Accounting & Finance Tools
The accounting program helps with financial processes such as bookkeeping, invoicing, expense management, dues, and tax reporting. These instruments play an important role in ensuring legal conformity and fiscal disclosure.
Examples: QuickBooks, Xero, FreshBooks
HR & Talent Management
HR applications can assist in managing personnel data, staff hiring, employee training, staff onboarding, payroll, benefits, and performance. They are supportive of compliance, reporting, and workforce planning as well.
Examples: Skill Lake, Workday, BambooHR, Gusto
AI-First & Intelligent Applications
AI-first applications are developed from an intelligent core, streamlining processes, boosting decision-making, and amplifying productivity through automated actions and thoughtful suggestions. These tools are progressively integrated into diverse business functions, enabling organizations to work more swiftly and more efficiently.

AI Content Creation & Automation
Such tools make the production of written, visual, or multimedia content possible with minimal human intervention. They have found extensive use in marketing, customer communication and design
Examples: ChatGPT, Gemini, Jasper, Copy.ai, Canva Magic Write
AI Code Assistants
By proposing code snippets, flagging errors, and crafting whole functions from natural language input, code assistants ease the work of developers. They accelerate the development process while cutting down on repetitive work.
Examples: GitHub Copilot, Amazon CodeWhisperer, Microsoft Copilot
Predictive Analytics & Business Intelligence
These platforms examine historical data and discover trends, forecast outcomes, and underpin strategic decision-making. These tools are routinely applied in finance, marketing, supply chain, and operations to assist with planning and manage risk.
Examples: Microsoft Power BI, Tableau, Qlik Sense
Conversational AI & Chatbots
Conversational tools imitate human interactions and are employed to raise the quality of customer support, speed up user onboarding, and respond to internal queries. They speed up response time, lower support expenses, and provide continuous service around the clock.
Examples: Intercom, Drift, Zendesk AI, ChatGPT integrations
Custom Applications
A custom application is an application specific to the requirements of a business, or may involve applications specific to processes or industry. These applications are more flexible and have control and the ability to integrate with their internal systems as compared to off-the-shelf products. They are a great fit for organizations looking to secure a competitive edge via technology that conforms to their operational needs.

Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
Using these platforms, users can deploy applications swiftly with only a minimal amount of coding knowledge. They provide a drag-and-drop interface, pre-configured components, and the capability of integration, which makes them the right choice when it comes to building internal applications or automating processes. No heavy development is required.
Custom Cloud-Native Apps
These applications are developed in cloud environments to be efficient and resilient. They accommodate complicated business applications, multiple users, and real-time processing of information. Built largely with contemporary frameworks, they can be thoroughly tailored and seamlessly connected to existing enterprise systems.
Mobile-First Custom Apps
They constitute tailor-made mobile applications crafted to enable business operations while on the move, field services, logistics processes, and customer engagement. They emphasize on responsive design, offline access, GPS capabilities, and mobile-native features like push notifications.
Modern Software Delivery Models: Scalable, Flexible, and Built for the Future
Software development, deployment, and delivery have changed radically. The new models of delivery include flexibility, scalability, and a reduced time-to-market. This helps businesses feel free to adapt to the changing needs of the users and infrastructure. The methods also allow modular development, on-going refinement, and wider device support, making software future-proof.
Cloud-Native Apps: SaaS, PaaS, FaaS
Cloud-native applications are designed to be run and scaled in the cloud without any challenges.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): Apps available as ready-made forms all over the internet (e.g. Google Workspace, Salesforce).
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): App development platforms that provide access to infrastructure to develop apps (do not need to manage infrastructure, eg., Heroku, Azure App Service).
- FaaS (Function as a Service): Serverless Forms under which code is executed as an outcome of events (as in the case of AWS Lambda, or Azure Functions).
Hybrid & Edge Applications
Hybrid apps utilize cloud-based systems and on-premise or edge computing to enable the use cases that need low latency, real-time data processing, or an offline state. The edge applications bring the data processing nearer to the source, which is suitable in the case of IoT, manufacturing, and field operations. This ensures they are less reliant on central servers and can act faster.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and Cross-Platform Development
Similar to native apps, PWAs provide app experiences through the web, with the same aimed focus as websites (reach) but with the capabilities of native applications, such as working offline and sending push notifications. Developers can write the code once and then deploy it on iOS, Android, and web using Flutter or React Native, with cross-platform development working to make delivery faster and far less expensive.
API-First and Headless Architecture
API-first requires all features to be available through APIs, which means that integration is flexible, platform-wise. The headless architecture separates the front-end from the back-end because it enables a business to publish content in a consistent manner on websites, mobile applications, smart devices, and so on. It is perfect in the case of omnichannel experiences and accelerated innovation.
Licensing & Monetization of Application Software
As a fundamental aspect of the software lifecycle, licensing and monetization are serious considerations for any institution that wants to make money, regulate its use, and govern intellectual property. Selecting the appropriate licensing model and monetization approach guarantees the sustainable development process, and its usefulness matches the expectations of the target audience and target market.
Here’s a breakdown of the key licensing types and monetization models:
Common Software Licensing Models
-
Proprietary License: The vendor owns the software and sells its rights to the user under specific conditions. It keeps the source code closed. A typical case is enterprise software.
Example: Microsoft Office -
Open Source License: The source code is commonly publicly available under licenses such as MIT, GPL, or Apache. The software can be used, modified, and expanded by any business as it deems fit.
Example: WordPress, Linux -
Freemium License: Provides some free-of-charge functionality and more complex functions or enterprise-level features at paid levels.
Example: Slack, Trello, ReachOut -
Subscription-Based License (SaaS): Customers use a subscription fee (monthly/annually) to get constant access to software that is stored on the cloud. It contains updates and support.
Example: Adobe Creative Cloud, Zoom, Infince Cloud -
Perpetual License: A fixed amount of money purchased will provide lifetime access to a particular version of the software. Future upgrades/support may not be included.
Example: Some legacy desktop applications
Popular Monetization Strategies
-
Pay-Per-Use / Usage-Based Pricing: Imposes billing charges per actual consumption- an optimal choice for APIs, serverless, or data-intensive applications.
Example: AWS, Twilio -
Tiered Pricing Models: Pricing is available on a tiered basis, such as feature, number of users, or limit of use. This is geared towards start-ups, SMEs, and enterprises.
Example: HubSpot, Notion, Skill Lake -
One-Time Licensing + Maintenance Fee: An intermediate model of selling software under a once-only license (with annual optional maintenance and support).
Example: Some ERP and desktop software packages -
In-App Purchases & Add-Ons: It is employed in SaaS and mobile apps primarily, where the extra functions, components, or online products are offered within the system.
Example: Mobile apps, design tools, productivity plugins
How to Choose The Right Application Software For Your Business
As your business grows, there's always an impulse to improve operations and get work done smarter. With the advancement of AI applications, there are a plethora of options to choose from. Whether it is to replace an old system or discover a new solution to modernize your inefficient performance, the hunt for the perfect application software is no cakewalk.
Picking the right application software for business involves wise decisions, brainstorming sessions, and critical thinking. Before investing in a software application, you must ensure that it aligns with your business operations, streamlines your processes, improves customer experience, and eliminates risk. The success of your business model, its anticipated goals, and its requirements depend on choosing the right application software. Selecting the right application software can be overwhelming, but the right one can become a real game-changer for your business!
Here's a checklist to help you be confident in choosing the right application software for your business.
- Define your expectations based on the pros and cons of your existing software, if any.
- Prioritize your business needs by determining application features you would like to have and an absolute must-have.
- Compile a list of application software that can provide the needed services and features.
- Validate your shortlisted software apps based on your budget, software license, and features.
- Conduct a complete evaluation, testing, or demo of the shortlisted applications- will they meet current and future needs?
- Zero down on the application software that can swing around all your needed requirements.
What is the Cost of Developing an Application Software?
Pricing is a crucial factor for anyone looking to develop an application for their business. The cost of developing an application software varies depending on the various features listed below.
- Functionality, scope, features, and purpose of the application software
- Platforms and devices supported
- Third-party integrations required
- Type of application: web, native, cross-platform, hybrid, etc.
- Back-end development
- Hardware components and compatibility
- The complexity of the application
- Maintenance and support requirements
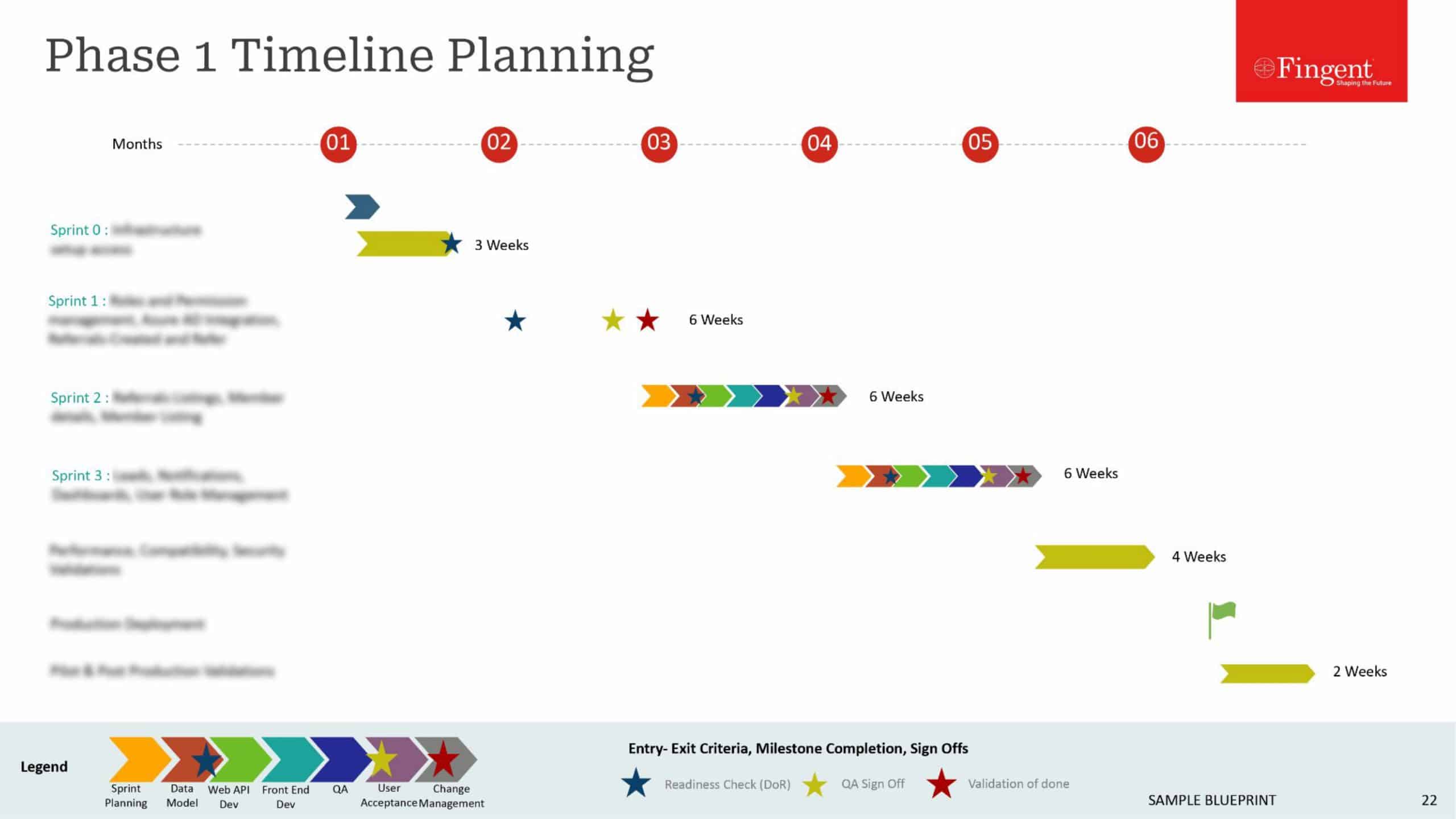
As many factors collectively influence application software development, it is difficult to quote a precise figure. However, depending on your requirements, our experts can get back to you with a ballpark estimate for your application software.
Key Trends Shaping Application Software Development in 2025
With the development of technology being quite fast, the software applications are increasingly getting smarter, more connected, and more integrally embedded into all the business areas. There are a number of trends that have been transforming how applications are designed, delivered, and experienced as a result of differing user needs, technological advancements, and organizational philosophies. Knowledge of such trends can enable businesses to future-proof their software investment and remain competitive.

AI-Integrated User Experiences
Apps are integrating AI or smart capabilities into the workflows to support users, either in content suggestions, intelligent work automation, personalization, or powerful analytics. AI is no longer an add-on feature; it is becoming an all-inclusive component of your daily workflow within productivity, CRM, or ERP system.

Cross-Platform Development
Organizations are engaging in the creation of mobile applications that do not only ease the interactions between mobile, desktop, and web, but often do so with a single codebase. Frameworks such as Flutter, and react native are facilitating this shift to make the development process faster and reduce maintenance activities.

Low-Code/No-Code Development
Apps can be built by non-developers using a visual interface and drag-and-drop editors. These solutions reduce the costs of development and easing the creation of the solutions as well as reducing the time of creating.

API-First Ecosystems
The API-first design allows the smooth linking of apps, services, and platforms. It promotes flexibility and extensibility features that are paramount to companies with numerous interdependent systems.

Cloud Computing
Cloud-native applications enable companies to dynamically scale, lower infrastructure expenses, and roll out updates. Models such as SaaS, PaaS, and FaaS enable fast innovation and presence at the global level. AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are some of the most prominent platforms.

Hyper-Personalization at Scale
Applications are learning more about user behavior, roles, and preferences in real-time to increase relevancy and engagement across applications used by customers and internally.

Composable Architecture
Applications are changing to modular rather than monolithic design in terms of microservices or packaged business capabilities (PBCs). This simplifies the process of component replacement, scaling functions, and accelerating innovation.

Cybersecurity-Embedded Design
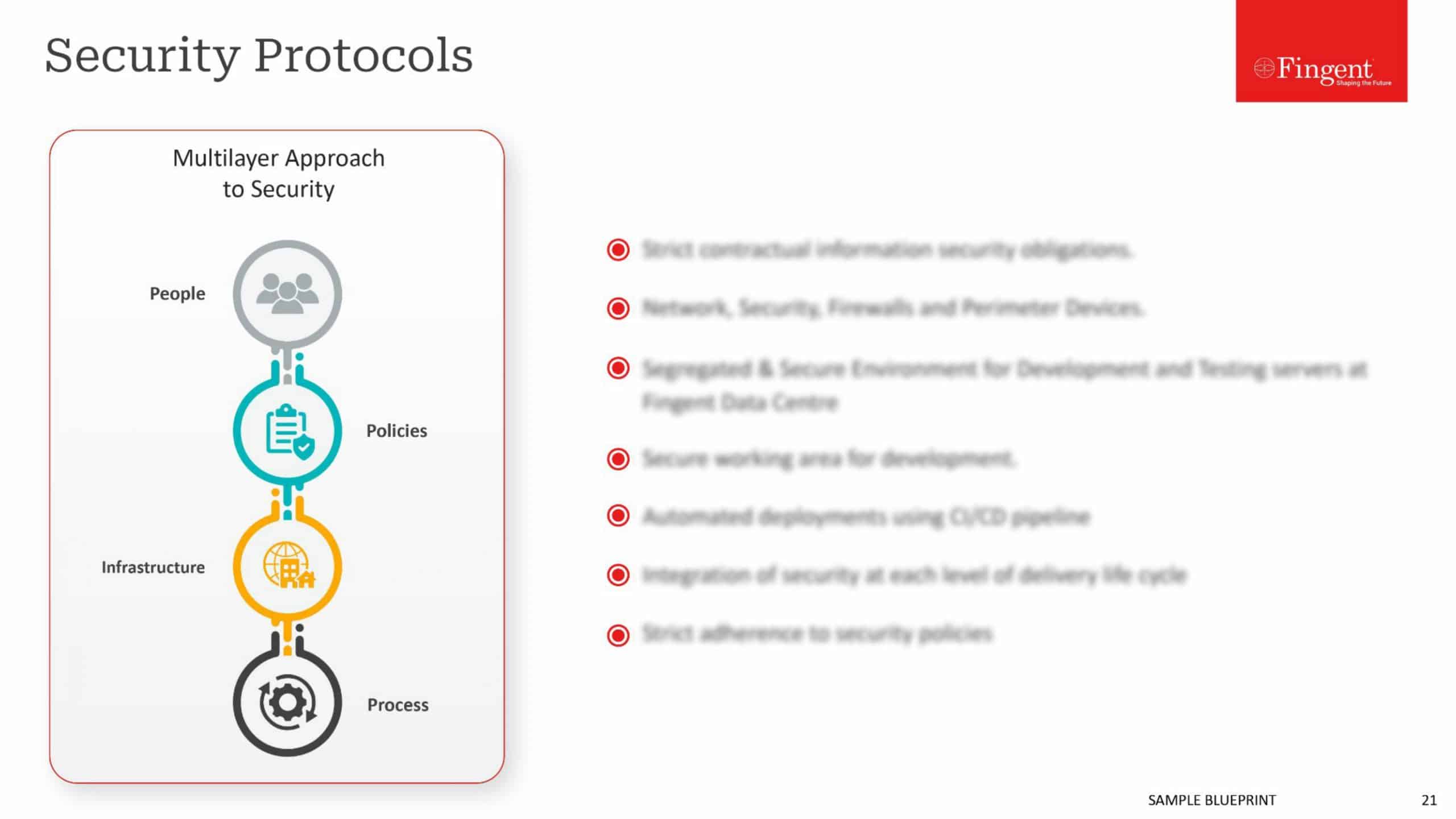
Security has become a central aspect of developing software. To safeguard delicate information and limit changing hazards, applications are constructed with encryption, secure verification, role-based permissions, and compliance backing.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between SaaS and traditional application software?
SaaS (Software as a Service) is a cloud platform where the software has subscriptions and can be accessed through the internet - nothing to install, nothing to maintain on the user end. A good example of SaaS is Microsoft 365. Traditional application software is generally deployed directly to local machines or servers and frequently has to be manually updated, as well as pre-licensed. Application software includes old versions of Microsoft Office.
2. How do AI-first applications improve productivity?
AI-first applications integrate smart capabilities into workflows themselves, including automation, intelligent recommendations, natural language interfaces, and predictive intelligence. This saves manual work, accelerates decision making, and enables users to concentrate on high-value activities.
Examples: Sorting inboxes using AI, automatic reports, and prioritization of intelligent tasks.
3. What is the difference between a mobile app and an application?
A mobile application is a special software application that runs on the smartphone or tablet or can be installed through app stores. The word application is an expanded term referring to any kind of software such as desktop, mobile or web-based and used to accomplish specific duties.
4. What is API-first development, and why is it important?
API-first development is an approach in which APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are central to both design and implementation. It allows anyone to integrate the application easily, has a modular structure, and can be connected to other systems, platforms, or services. This would enhance flexibility, speed up development, and offer natural cross-platform experiences.
5. What are Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and how do they benefit businesses?
PWAs are web sites which provide the functionality of native apps (including offline, push-messages, and the ability to be installed on the home screen) all through a browser. To companies, PWAs are cheaper to create, have wider device coverage and are reliable in features and rapid delivery of user experience that do not require separate mobile apps.
6. Is low-code/no-code development applicable to enterprise applications?
Indeed, low-code/no-code solutions are gaining popularity in the work of enterprises to develop their own tools, automate business processes, and expeditiously develop prototypes. They might not be a complete substitute to fully custom-built systems in complex use cases, but they greatly reduce the project time, IT dependency and enable the employees in any business department to make a solution adapted to their needs.
Top Emerging Technologies in Application Software

Generative AI
An AI model that can generate content like text, graphics, and code is changing applications in marketing, software development, customer support, and design. They facilitate hyper-efficiency, personalization, and automating creativity.

Virtual Reality (VR) 2.0
Next-gen VR can be more immersive, responsive, and life-like. It is used in simulation, remote training, design visualization, and virtual collaboration in industries.

Augmented Reality (AR)
AR is superimposing digital content on the physical material. It improves customer experience, training on the side, support, remote assistance, and visualization of products, particularly in the retail, field services, and manufacturing sectors.

Internet of Things
IoT is designed to link real-world devices with software so that they can be monitored and automated in real-time and generate analytics in real-time. They are used in smart factories, logistics, energy supply and healthcare systems.

5G Expansion
5G offers rapid data transmission and ultra-low latency, enabling real-time technologies like self-driving cars, remote surgery operations, smart towns, and augmented or virtual reality applications on a large scale.

Biotechnology in Agriculture
High-end software is becoming a part of bio technology data to monitor crops, perform gene editing and precision farming in agriculture- increasing the yield, sustainability and disease resistance.

Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous cars navigate by performing tasks through software that analyzes real-time data, which comes in the form of sensors and maps. New applications facilitate route planning, fleet control, and anticipatory treatment.

Blockchain
In addition to cryptocurrency, blockchain finds applications in secure data sharing, smart contracts, supply chains, and digital identity management, ensuring transparency and decreasing fraud.

Edge Computing
Edge computing analyzes data near the origin (e.g. IoT devices), leading to the minimization of latency and bandwidth consumption. It facilitates real-time-sensitive systems in the manufacturing, healthcare, and retail sectors.

Wearable Health Monitors
These devices are real-time biometric devices, and they play an important part in monitoring patients remotely (health monitoring applications), fitness applications, and emergency warning systems in the medical field.

Extended Reality (XR) for Training
AR + VR + MR is being used to train employees through hands-on usage, simulations, and skill training in areas such as medicine, defense, and many more, which has made them very useful in enhancing engagement and retention.

Voice-Activated Technology
Software voice interface is making the field more accessible and hands-free, particularly in smart homes, automobiles, and enterprise productivity applications such as virtual assistants.

Advanced Robotics
In logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing, software applications are being embedded into robotics AI-based technologies to control and monitor processes on a large scale, automate, and increase precision.

Telemedicine
Telemedicine apps also make it possible to diagnose, treat, and monitor a patient remotely. The solutions enhance access to healthcare, make it less expensive and convenient for the providers and patients.
Develop Your Application Software With Fingent
As online transactions soar and digital workplaces emerge, different types of application software will continue to evolve. As a result, the demand for custom software development tailored to a business's requirements is increasing now more than ever before. From simple customizations to full-cycle application development, Fingent can help address all your specific business requirements, leveraging our application software development capabilities. Explore our range of services.
20+
Years of Experience
400+
Qualified Professionals
700+
Completed Projects
8
Centers of Excellence

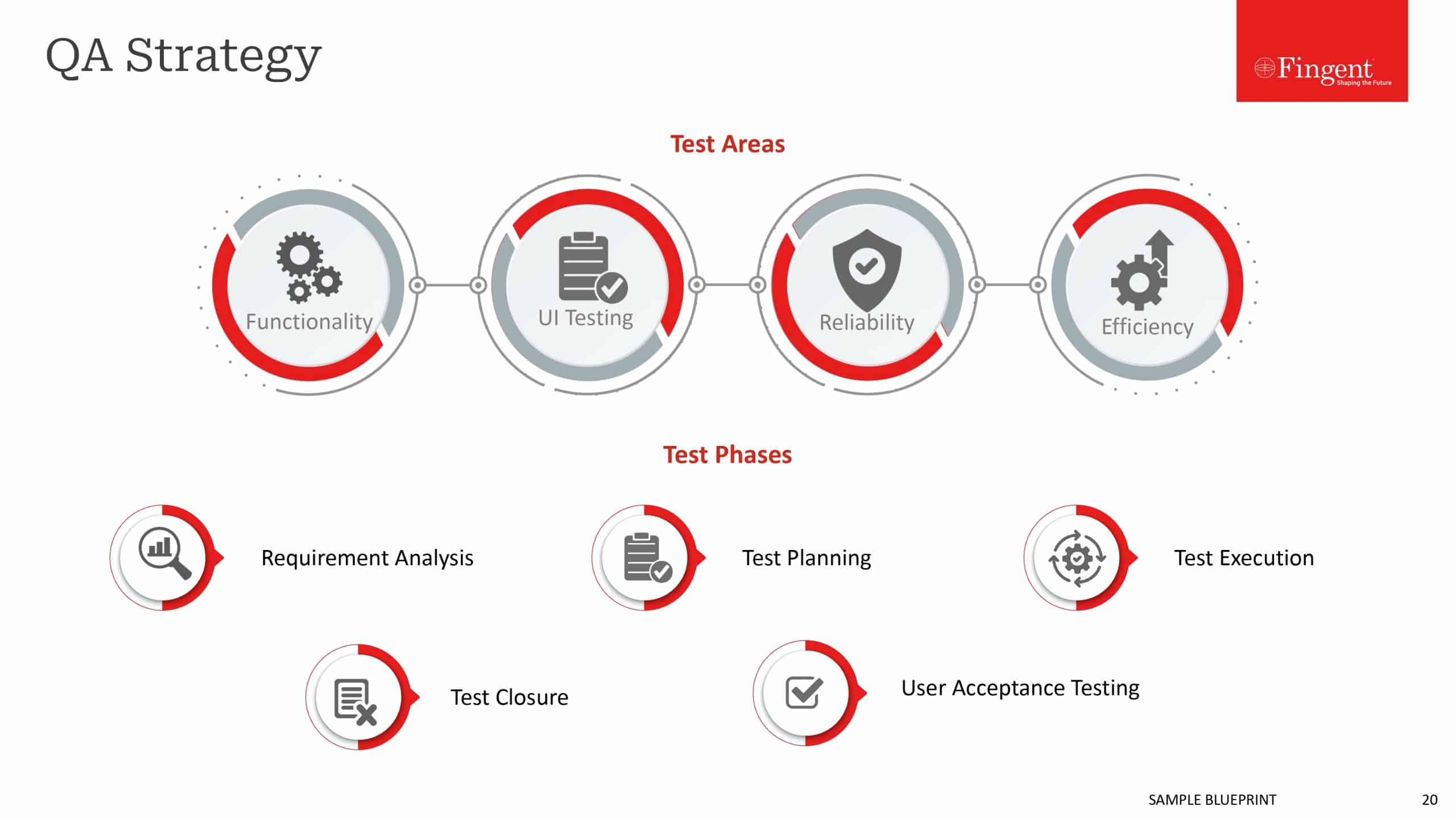
Dedicated QA Practices
Transparent Project Management
If you have further questions or want to start choosing and implementing the right application software for your business, contact us immediately. We will help you get there.

 US
US Insurance
Insurance