Table of Contents
- Criteria to Select The Right Cloud Service Provider
- How Can Cloud Support Your Custom Software Needs?
- SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS: Which Cloud Service Model Fits Your Business?
- Top Cloud Computing Trends To Follow
- How Does Fingent Help You Adopt The Right Cloud Service Model?
- Frequently Asked Questions on Cloud Service Models
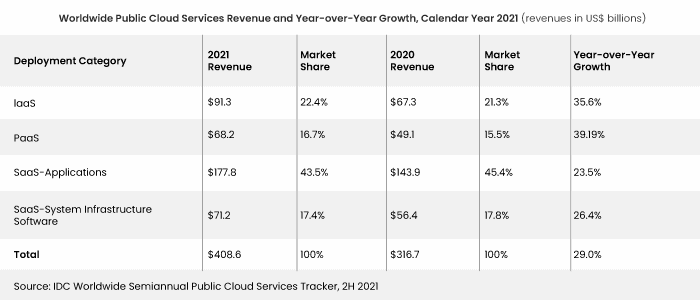
A Quick Introduction to Cloud Service Models
Are you looking for a Cloud Service Provider?
Why Does Your Business Need Cloud Computing?
High Performance and Availability
Cloud services are distributed across multiple cloud facilities. This eliminates your downtime, ensuring high availability. Your cloud service provider will be responsible for updating cloud systems, fixing bugs, and solving security issues in the cloud. The performance gains offered by cloud is higher than that of on-premise infrastructure.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud computing allows you to quickly scale up or down your computing resources and storage to meet the changing business needs. You don’t have to invest heavily in any physical infrastructure to support the changes, such as an increase in the load levels.
Effective Collaboration
Cloud storage makes your data available anywhere, anytime you need it. Location or device constraints don’t prevent you from accessing your data from anywhere in the world. As long as you have a stable internet connection and a computing device (a laptop or smartphone) in your hand, you can collaborate effectively with anyone, in any part of the world.
Cost Savings
When you choose a cloud service model, you only pay for the resources that you actually use. Most cloud computing services are pay as you go or pay per use. This is a great money saver for startups and small businesses with lower budgets. Your IT team doesn’t have to overbuild or overprovision your data center, so they get more time to focus on strategic work.
Advanced Security
Centralized data backups in the cloud provider’s data centers eliminate the need for maintaining your own backups onsite or offsite. This mitigates the risk of data loss in the wake of a disaster. Cloud providers can help restore your data from the cloud storage, which is automatically updated in real-time. To provide more robust protection, you can implement cloud security techniques, such as data encryption and two-factor authentication
What are Cloud Service Models?
Adopting Cloud – Choosing Between SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS
SaaS
SaaS Benefits
- Lower up-front costs and TCO: SaaS eliminates the need for additional hardware and software, reducing the installation and implementation costs.
- Anywhere accessibility: With SaaS, you can access cloud services from anywhere using an internet-enabled device such as a smartphone or laptop. SaaS eliminates the physical constraints of on-premise software.
- Ready to use: You can quickly set up SaaS services, so they become fully functional in minimal time. All it takes is that you sign up for the service (pay on-demand) to get access to fast and powerful computing resources.
Why Should You Opt SaaS?
Points to Consider Before SaaS Implementation
- Opting for “configuration over customization” will allow you to tailor the SaaS solution without extensive customization. This saves your time as you don’t have to worry about scaling with constant updates and documentation.
- Understand the adoption and usage rates of the SaaS solution carefully, and set clear objectives that you want to achieve with the SaaS adoption.
- Complement your SaaS solution with third-party integrations and advanced cloud security options to make it more user-centric, secure, and data-driven.
IaaS
IaaS Benefits
- Lower costs: IaaS cloud model eliminates the need to deploy expensive on-premise hardware. Developers, DevOps, and DevTest teams get more freedom to experiment and innovate by saving the time and money spent on provisioning and scaling environments.
- On-demand availability and scalability: As the most flexible cloud computing model, IaaS allows you to scale the computing resources up or down rapidly according to the needs of your enterprise.
- Faster time to market: IaaS ensures faster development cycles by allowing you to quickly spin up the necessary computing infrastructure. You don’t have to wait for weeks and months for it to be ready.
Why Should You Opt IaaS?
Points to Consider Before IaaS Implementation
- Consider your technical, storage, computing, and networking needs while looking to implement an IaaS solution.
- Data security is highly important while evaluating cloud services and providers.
- Look for disaster recovery features, server size, throughput of the network, and the general manageability requirements.
PaaS
PaaS Benefits
- Speed to market: Your cloud provider does all the heavy-lifting by providing your developers instant access to a complete application development platform, which is built and managed by them. It gives your team more time to develop and deploy.
- Mitigates security risks: Your PaaS provider is responsible for securing the infrastructure. The PaaS model strengthens security by increasing business resiliency, reducing downtime, preventing data loss, and accelerating recovery.
- Bolsters IT efficiency: PaaS standardizes deployments, improves scalability, pushes automation of routine tasks, and speeds provisioning to make your IT more responsive to innovative business opportunities. For example, PaaS accelerates your release cycles using containers and APIs, and enhances data recovery and analytics.
Why Should You Opt PaaS?
Points to Consider Before PaaS Implementation
- Ensure you can easily scale with your PaaS provider and they have all the options available which you need.
- Check if the PaaS solution is optimized for the language and framework you’re using. Otherwise runtime will be affected.
- Decide where you want to deploy your application - on a private or public cloud.
- Identify the level of automation and customization you require - whether it needs to be self-service or fully automated.
Want to know which cloud service model fits your business?
Why is it Important to Choose the Right Cloud Service Model?
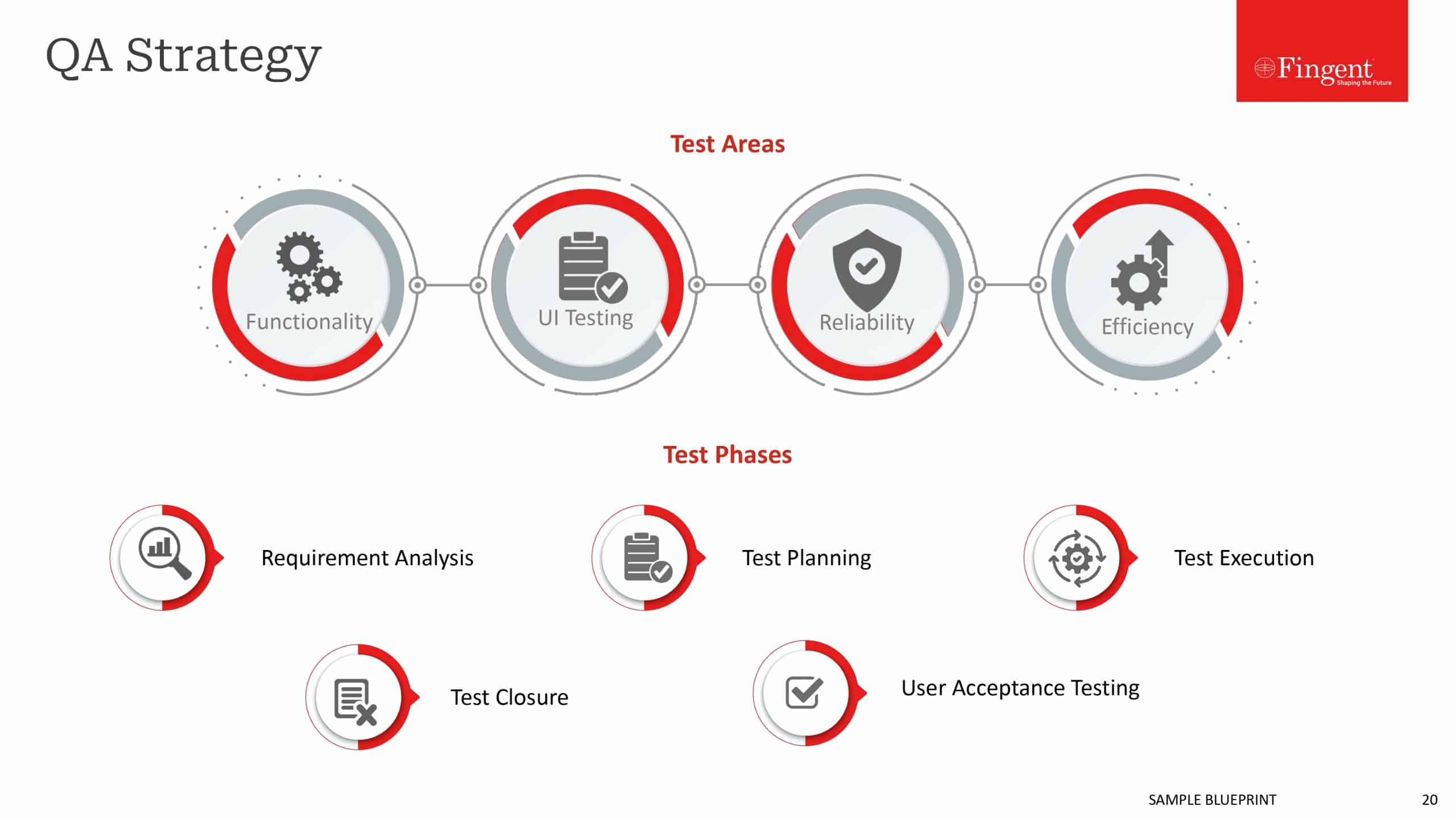
Criteria to Select The Right Cloud Service Provider
- Verify if the cloud service provider complies with recognised standards and quality frameworks. Look for vendors who are accredited with certifications such as ISO 27001.
- Evaluate the service provider’s technologies and service roadmap for development. Ensure their platform and technologies align with your cloud objectives and IT environment. Find out if their service roadmap fits your requirements in the long term.
- Look for providers who give you choice and control regarding the jurisdiction in which your data is stored, processed and managed. Make sure the provider’s data loss and breach notification processes are aligned with your organization’s data governance and risk management obligations.
- Assess the cloud provider’s service dependencies and partnerships, including multiple vendor relationships, connected components, subcontractors, implications of service dependencies on SLAs, accountability, responsibility, service disruption policies, and limitations of liability.
- Get clarity on the roles and responsibilities related to services and deliverables, contracts, SLAs, policies related to security, data management and conversion, backup and resilience provisions, legal protection, pricing models, exclusions, caveats, remediation policies, and penalties.
- Analyze if the provider follows an established, documented, and proven process to manage planned and unplanned downtimes. Evaluate their ability to support your data preservation expectations.
- To avoid the risk of vendor lock-in, look for providers who use minimal proprietary technology. This increases your ability to migrate or transition to a competitor cloud service, based on your growing business needs.
- Finally, assess the technical and operational capabilities of a cloud service provider by evaluating their company profile and portfolios, client reviews, analyst profiles, ratings, and market position. Cloud providers who run a sound business offer the most compatible and competitive cloud service.
How Can Cloud Support Your Custom Software Needs?
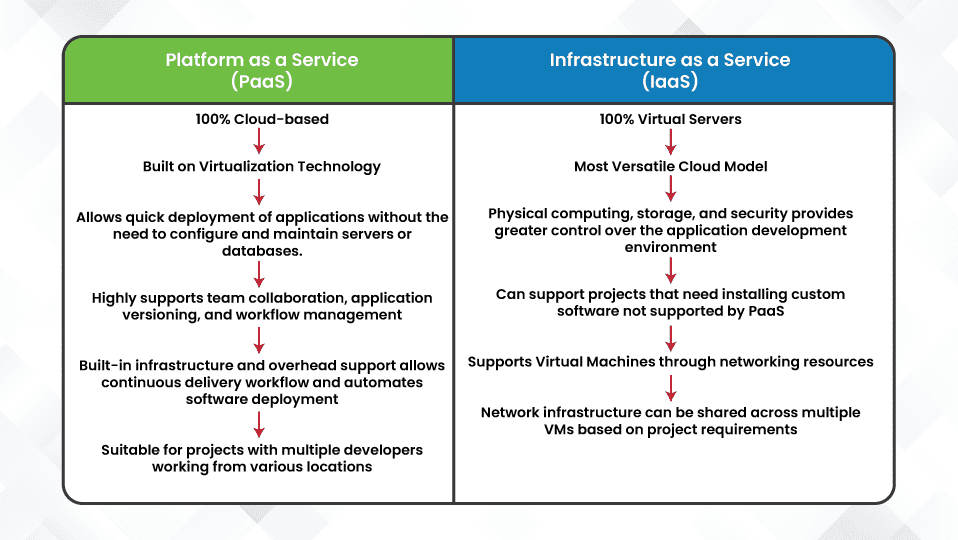
SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS: Which Cloud Service Model Fits Your Business?
When Do You Need SaaS?
- Benefit from application usage without the need to maintain and update infrastructure and components
- Don’t want to reinstall applications or purchase new licenses each time you switch to a new device
- Cut down on internal IT overhead and retain only your subscription cost of the SaaS application
- Gain more compute power and database storage depending on your usage. Your SaaS provider handles scaling up the application.
- Great deal of flexibility to operate from any device, any location, any time
- Great deal of flexibility to operate from any device, any location, any time
When Do You Need IaaS?
- Consolidate heterogeneous disaster recovery systems into one virtualized environment
- Perform big data analysis that requires a lot of processing power
- Manage unexpected traffic spikes by scaling on-demand
- Get new projects up and running quickly, according to changing business priorities
- Overcome application performance limitations caused by capacity constraints
- Experience business growth that outstrips infrastructure capabilities
When Do You Need PaaS?
- Develop or host new custom applications without any hassles and costs of installing hardware or software
- Free your developers to focus on their application code through simpler, faster, and secure app development
- Analyze and mine your data, find insights and patterns, and predict outcomes to improve forecasting, product designs, ROI, and other business decisions
- Use sophisticated software development kits and BI and analytics tools that you can’t afford to purchase outright
- Develop for multi-platforms, including mobile and web browsers using the same code base
- Implement agile methodologies that allow you to test and prototype new applications more quickly than usual to gather user feedback
Looking For Experts To Discuss Your Cloud Requirements?
Top Cloud Computing Trends To Follow
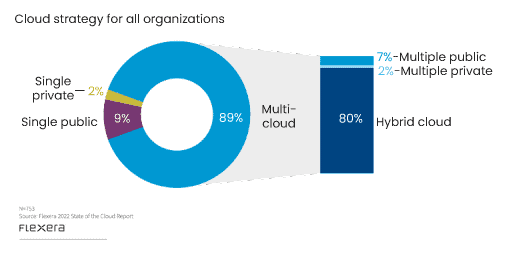
1 Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud
| Example of Multi-Cloud | Example of Hybrid Cloud |
| An organization hosting its web front-end application on AWS, while keeping its Exchange servers on Microsoft Azure | Combining your on-premises data center with a public cloud computing environment like Google Cloud |




 US
US Insurance
Insurance