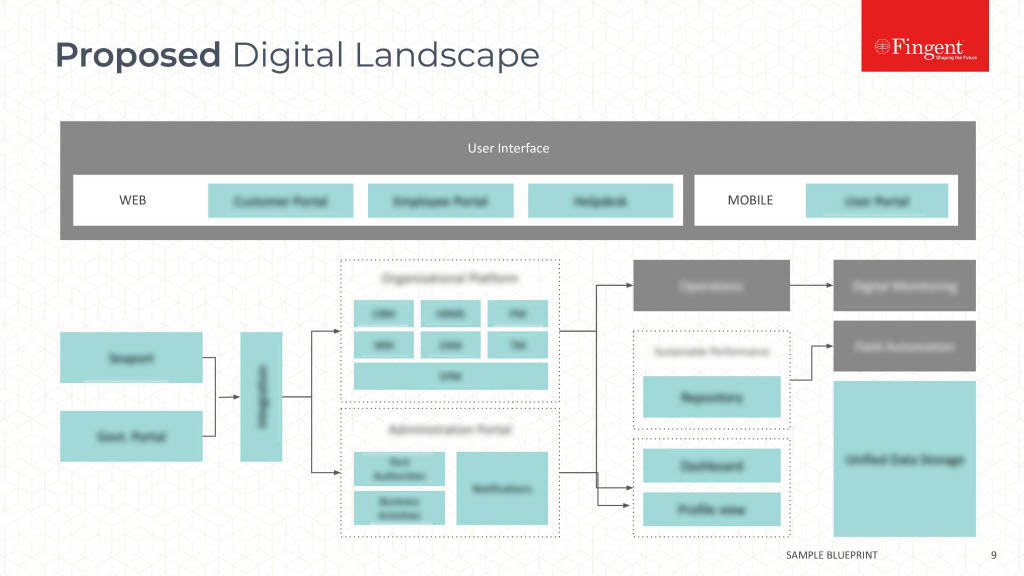
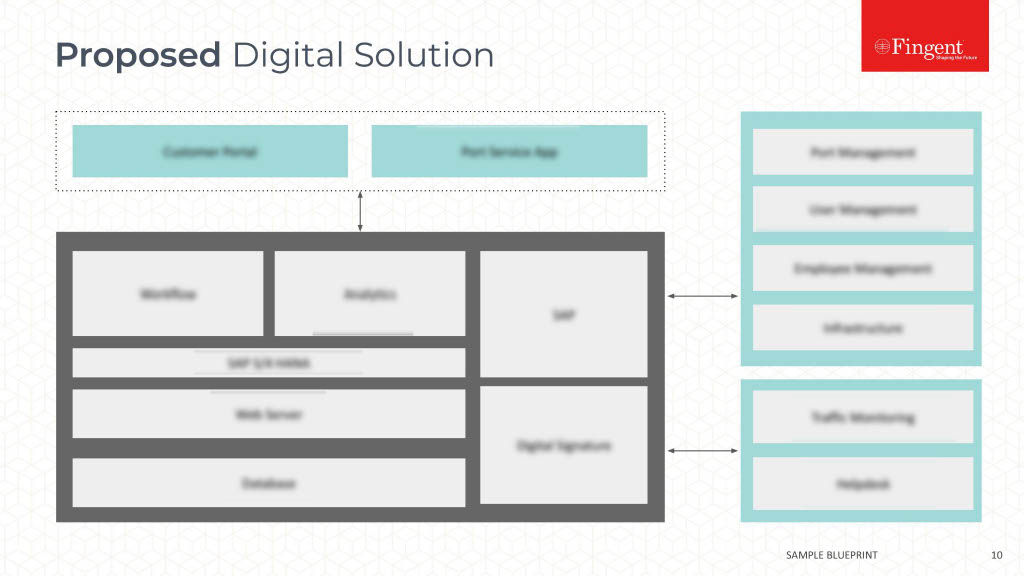
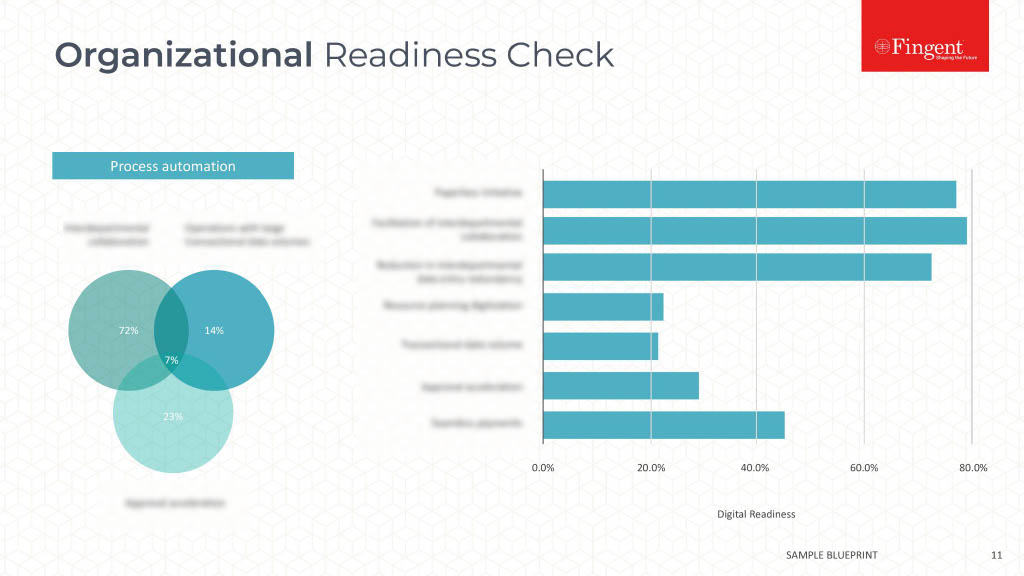
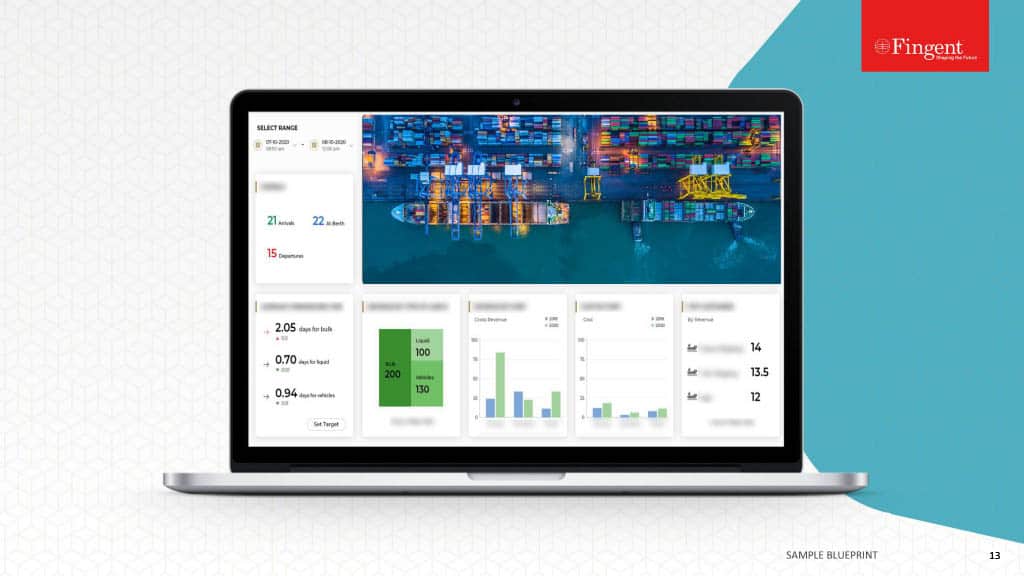
Table of Contents
Effective Equipment Maintenance: A Business Imperative

“Give me six hours to chop down a tree and I will spend the first four hours sharpening the axe.”
– Abraham Lincoln
While it’s true that nothing can replace regular preventive maintenance, several businesses fail to keep it on their priority list. Everyone knows that equipment maintenance isn’t a piece of cake as it involves managing costs, labor, expertise, inventory, testing, and a myriad of activities. At the same time, effective equipment maintenance is a business imperative that you can’t just overlook.
That said, how can you streamline your company’s equipment maintenance process without missing a beat?
Enter Augmented Reality, the most innovative and impactful technology that can ensure the longevity of your machinery, optimize your equipment maintenance budget, reduce manual effort, and mitigate any loss occurring due to negligence or delayed attention.
If you consider equipment maintenance a more viable and convenient strategy than investing in new fixed assets, it’s important to understand the role of Augmented Reality in simplifying equipment maintenance.
What is Augmented Reality and How Does It Support Equipment Maintenance?
Augmented reality (AR) is an interactive experience technology that overlays digital information (augmented components) and graphics on top of the real-world environment to enhance our perception of the physical objects around us.
AR has many potential applications in various fields, including equipment maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO). For example, an AR app can display the 3D model of a machine along with its components and relevant instructions on how to repair or service it. A technician can interact with the data superimposed on an equipment’s surface to repair it safely or even remotely without taking much time.
With AR-based applications, your maintenance personnel or service engineers can:
- Examine and monitor engine parts and focus deeply on machine faults
- See the detailed 3D preview of a machine or engine in motion
- Analyze airline maintenance operations with greater accuracy and efficiency
- Perform preventive and corrective maintenance of critical equipment
- Bring more transparency into equipment audits and surveys
- Facilitate performance modeling, benchmarking, and simulation of equipment
- Support industrial equipment risk identification and management

Benefits of Using Augmented Reality in Equipment Maintenance
Augmented Reality brings a fundamental shift to the traditional approaches followed in operator training and maintenance of industrial equipment and assets. Introducing Augmented Reality in Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul functions offers numerous benefits to your business:
1. Augmented Visualization
AR-powered headsets, mobile-devices, or wearables can overlay digital information such as 3D models of complex equipment, along with detailed virtual maps, diagrams, and instructions onto the real-world environment. For instance, when a technician is inspecting an industrial asset, the enhanced visualization superimposed by AR on the technician’s field of vision allows them to understand the equipment complexity, identify components, and locate issues quickly and accurately.
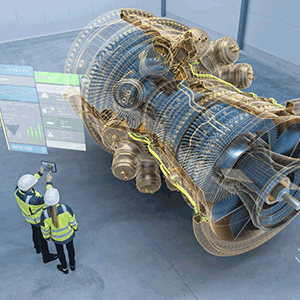
2. Real-Time Guidance To Maintenance Crew
AR can provide real-time guidance and step-by-step instructions to your on-site equipment maintenance personnel, so they don’t have to attend extensive and monotonous training or refer to complex instruction guides or user manuals. Technicians can follow the visual cues and annotations overlaid on the equipment parts in real-time to ensure precise execution of maintenance procedures and minimize errors.
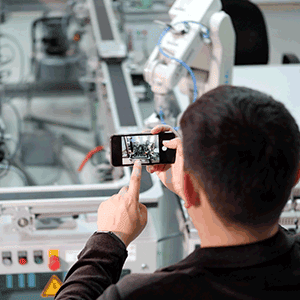
3. Remote Support & Collaboration
AR enables your subject matter experts and senior employees to provide remote guidance and support to on-site technicians engaged in maintenance jobs. Through AR-enabled smart glasses or mobile devices, technicians can live-stream their view to the remote SMEs who can provide real-time instructions or annotate/ draw directly on the technician’s field of view. This capability enhances field team and back-office collaboration, reduces travel costs, and speeds up problem resolution.
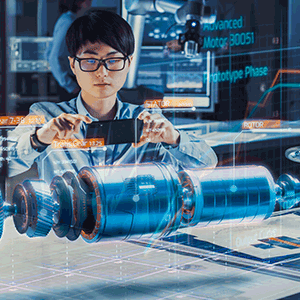
4. On-Demand Information Access
AR provides your maintenance personnel with on-demand access to relevant information including equipment specifications, maintenance history, troubleshooting tips and guides, and virtual service manuals. Technicians can access this information hands-free, directly within their field of view using AR headsets, smart glasses or other wearables, and complete the maintenance or repair job with improved efficiency and minimal downtime.

5. Training & Skills Development
With AR-based training, existing maintenance crew can upskill themselves, while new technicians can learn more about complex equipment and maintenance procedures in a more interesting way. By overlaying interactive virtual instructions and simulations onto physical equipment, AR provides a safe and immersive learning experience to maintenance technicians. Trainees can practice complex maintenance tasks, identify faults, and learn correct procedures – all in a safe virtual environment, before working on actual equipment.

6. Predictive Maintenance & Data Analytics
AR-integrated equipment maintenance systems can gather data from device sensors and connected Internet of Things (IoT) devices to perform real-time equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance analysis. By visualizing the health and performance of equipment in real-time, technicians can proactively identify potential failures, monitor performance metrics, and schedule maintenance tasks based on actual equipment conditions. This helps in optimizing maintenance schedules and maximizing uptime.

7. Documentation & Record-Keeping
Accurate and up-to-date documentation of equipment maintenance activities is important for planning and scheduling future maintenance jobs. In case of recurring maintenance activities, these references come handy. Using AR, maintenance personnel can capture images, videos, and annotations during the repair process, which can be automatically logged and stored for future reference. This digital record-keeping improves knowledge retention, enables better analysis of historical maintenance data, and helps address compliance requirements.

Benefits of AR in Equipment Maintenance: A Snapshot
Reduces mean time to repair
Faster problem diagnosis
Improves equipment availability
Minimizes unplanned downtime
Consistent servicing performance
Fewer errors in installation or servicing
Saves time and travel expenses
Top AR Use Cases in Equipment Maintenance
AR software solutions and applications have a broad scope of use in equipment maintenance, repair, and overhaul functions. Here are some of the top AR use cases in equipment maintenance.
AR can overlay visual instructions and annotations onto the equipment, guiding technicians through the repair process step by step. The AR system can highlight the parts to be inspected or repaired, display 3D models of how components fit together, and provide textual or audio instructions. This helps technicians perform repairs accurately and efficiently.
Instead of relying on traditional paper manuals or exhaustive digital documents, AR helps create interactive virtual user manuals that provide technicians with relevant data required to fix a specific equipment fault. Using AR-enabled devices like smart glasses or customized AR mobile apps, technicians can view step-by-step instructions overlaid on the equipment or receive real-time guidance, highlighting the parts to be inspected or repaired, along with relevant information.
AR helps create detailed virtual representations of equipment or machinery, allowing technicians to interact with them virtually before performing any actual maintenance task. Equipment simulations allow technicians to familiarize themselves with complex machinery, understand the functioning specifications, anomalies, and parts of the equipment, and practice troubleshooting procedures before attempting the steps on a real machine.
Digital twins (virtual mockups) of machines are created by equipment manufacturers to test the performance and drawbacks of their products before market launch. By integrating AR with the virtual replica (digital twin) of a physical equipment, technicians can compare in real-time the capabilities, data, output, and performance of the physical equipment through its virtual counterpart. This helps identify discrepancies, detect anomalies, and simulate “what if” scenarios for improving the equipment production line as well as planning predictive maintenance.
Equipment manufacturers as well as users often find it difficult to properly identify faulty equipment parts and order replacements. AR-enabled devices help scan the equipment, recognize the parts that need to be replaced, and provide maintenance technicians with relevant information such as part numbers, specifications, and inventory availability to simplify their jobs. Technicians can then place orders directly from the AR interface and track their orders end-to-end, which will streamline the whole procurement process.
The integration of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Augmented Reality (AR), and Big Data can revolutionize equipment maintenance practices. By leveraging IIoT, equipment is equipped with sensors and connected to a network, allowing real-time data collection and analysis. AR overlays digital information onto the physical equipment, providing maintenance technicians with intuitive visualizations and step-by-step instructions for efficient troubleshooting and repairs. Big Data analytics processes the vast amount of collected data, uncovering patterns and predictive insights to optimize preventive maintenance schedules and identify potential failures. This integrated approach enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, extends equipment lifespan, and improves overall maintenance effectiveness. The use of IIoT, AR, and Big Data in equipment maintenance brings significant cost savings, improved productivity, and a proactive approach to equipment care.
Real-Life Examples of Using AR in Equipment Maintenance
Success Stories of Augmented Reality in Equipment Maintenance
Example 1: Bosch
Bosch Automotive leverages Augmented Reality to accelerate motor-vehicle repairs and support technical training of workshop employees.
- Smarter and faster fault diagnosis and repair instructions with all the information displayed where needed
- 15% time saved by technicians per step taken when performing repair tasks
- Location of hidden components, instructions, or required special tools are integrated into the real image
- Clarifies the next steps to be taken in order to avoid unnecessary disassembly and assembly work
Example 2: DHL
DHL Supply Chain employs AR-based “Vision Picking” smart glasses in their warehouses to speed up the picking process and reduce errors.
- 25% efficiency increase during the picking process
- Hands-free order picking at a faster pace with reduced error rates
- Pickers equipped with smart glasses that visually display where each picked item needs to be placed on the trolley
- Workers can provide more complex value-added services to customers and accelerate new employee onboarding time
Example 3: Boeing
Boeing, the premier manufacturer of commercial jetliners, leverages Augmented Reality to advance fighter pilot training.
- Boeing’s next-generation fighter jets T-7 and F-15EX offer pilots a safe augmented reality training environment
- Pilots and ground operators can see synthetic threats in real-time, outdoors, and critically, in high-speed environments
- Real-time 3D visualizations to increase the efficiency of mission planning, briefing, and debriefing
- Tactical training scenarios delivered through AR reduce the cost of and need for multiple platforms and real world training exercises
Industries That Use AR for Equipment Maintenance
1. Automotive Maintenance
Automotive Diagnostics
Remote Expert Support
Proactive Maintenance
Intelligent Troubleshooting
Automotive Diagnostics
AR glasses integrated with the vehicle diagnostics software of the automotive manufacturer allow a mechanic to remotely inspect a vehicle’s condition, avoid potential downtime by reducing the time-to-repair, and cut down automotive maintenance costs.
Remote Expert Support
Complex vehicles with more maintenance needs require technicians to acquire specialized skills to service the cars properly. With AR-integrated digital twins, remote automotive experts can virtually demonstrate how to fix a part or component, so the on-site mechanic performing the repair can retain the knowledge and increase their efficiency.
Proactive Maintenance
AR-based applications integrated with predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms can analyze vehicle data to foretell the timing of a repair. This allows consumers to optimize the usability and life of expensive components or vehicle body parts. Trend-based analysis performed by extrapolating the run data and history of a component will help avoid potential safety issues and eliminate unnecessary repair costs.
Intelligent Troubleshooting
An AR device can receive and process the data observed by a car mechanic to enhance their field of view to propose the next step. AR provides the mechanic with a guided process to examine and trace the issue, leaving no chance for any guesswork. This can save significant time and improve first-time fix ratios.
2. Aircraft Assembly & Maintenance
Aircraft Assembly
Pre-Flight Checks
Maintenance and Repair
Personnel Training
Aircraft Assembly
Aircraft manufacturing or assembling is a complex process that requires utmost attention and expertise. Using AR technology, aircraft assembling instructions can be made available as 3D drawings superimposed upon the actual equipment, showing how the tasks need to be done step-by-step.
Pre-Flight Checks
Pilots or cabin crew can use Head Mounted Displays (AMD) based on AR technology to create and use a virtual checklist to perform pre-flight checks, depict runway information and piloting instructions to approach designated runways, and receive alerts related to other flights taking off, landing, or taxiing.
Maintenance and Repair
AR presents a cost-effective, safe, and time-saving alternative to using tedious maintenance manuals for routine maintenance checks or repairs. With a combination of AR, 3D scanning, sensors, analytics, and AI, technicians can get real-time details right in front of them, so they can perform comprehensive inspections, collaborate with off-site specialists, and complete maintenance or repair tasks without any distractions, misinterpretations, or downtimes.
Personnel Training
AR helps provide immersive on-the-job training for maintenance personnel and technicians in a safe, hazard-less environment. The best part is you can repeat training as many times as you want until your crew members become more proficient, without charging any additional costs. AR glasses can be used to train aircraft engineers by simulating and testing maintenance scenarios or processes. This helps reduce the risk of errors that could seriously impact lives.
3. Energy & Utilities Maintenance
Asset Maintenance
Employee Training
Remote Assistance
Operational Safety
Asset Maintenance
The ability of AR technology to overlay a 3D model on a piece of equipment goes a long way in improving the speed and efficiency of asset maintenance in energy and utility sectors. Field technicians can use AR mobile devices or smart glasses to immediately access operational documentation, check out the asset type can category, and go through the maintenance history or replacement conditions of the asset.
Employee Training
AR enhances the learning process by incorporating interactive virtual objects to the real-world environment, such as images, videos, and other forms of motion graphics. Utility personnel can access the components, work instructions, or detailed guidance they need right in their field of vision, so they can better understand how the asset should function ideally in a given situation. Thus, AR helps energy and utility companies to make their workforce highly qualified and competent.
Remote Assistance
AR can significantly lower your expenses on recruiting subject matter experts (SMEs). The technology allows your highly experienced employees to remotely guide novice or junior field workers in real-time. Sitting at the back-office, SMEs can give their eyes, ears, and hands on the ground by accessing immersive 3D projections of heavy equipment and sites. In a way, leveraging AR for remote assistance allows you to effectively utilize the skills of your retired or aging workforce.
Operational Safety
Connected AR glasses and smart AR wearable devices are used by energy and utility service engineers to model underground facilities, detect potential problems in heavy equipment, and reduce catastrophic failures. AR allows off-site supervisors to visualize safety protocols implemented in real-time on the worksite, analyze if employees comply with the safety regulations, and take actions to improve productivity and occupational safety.
4. Manufacturing Equipment Maintenance
Maintenance Training for Military Equipment
Reduce Equipment Downtime
Asset Identification
Review Equipment Indicators
Maintenance Training for Military Equipment
AR technology enables military personnel to get trained in machinery maintenance process by experimenting and training on virtual equipment. Since it’s not practical to disassemble a real piece of equipment repeatedly, AR technology can be used to simulate the internal structure and disassembly process of the equipment without disassembling it actually. Knowledge saved in the form of animation, voice and text can be used for repeated training in future.
Reduce Equipment Downtime
AR helps reduce the downtime associated with machine maintenance operations by allowing technicians to instantly access and apply detailed instructions in real-time. For instance, using a customized AR headset, a technician can view the 3D model of a car engine from any angle, rotate it in real-time to get a better look at specific components, and zoom in for a closer view. Once the technician completes a step, the 3D model automatically moves to the next step, guiding the way.
Asset Identification
When servicing a piece of equipment in a manufacturing floor, AR enables technicians to accurately identify the model, make, and other specifications of the equipment by leveraging the data stored in the manufacturer’s software. Real-time availability of data such as the machine’s maintenance history, parts used in the past, and new parts required will allow technicians to quickly identify, repair, or replace the components as needed.
Review Equipment Indicators
Manufacturers can access live equipment data such as machine temperatures, humidity levels, and pressure settings within their factory unit by using a series of sensors connected to an AR application or headset. For instance, monitoring a facility’s HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system will allow its supervisor to take immediate actions that can help ensure optimal working conditions within the facility.
5. Medical Equipment Servicing & Maintenance
Medical Equipment Servicing
Device Operator Training
AR Annotations To Improve Device Design
Medical Equipment Marketing
Medical Equipment Servicing
Complex medical equipment with numerous hardware/software components can be easily serviced, and issues can be resolved remotely with mobile AR applications that provide remote assistance. Technicians can instantly access AR data (voiced guide, tips, scenario steps) more relevant to the problem and make decisions with better confidence. Thus, the application of AR technology in servicing medical equipment reduces downtime and human intervention.
Device Operator Training
AR-based virtual training allows lab technicians and medical equipment operators to gain in-depth theoretical knowledge and practical expertise in using the equipment safely while adhering to the device standards and usage protocols. Training simulations, animated instructions, and 3D models powered by AR improve learning outcomes through enhanced skill acquisition and retention. Instead of trying out a medical device in a real scenario, technicians can use digital twins or virtual replicas to test the device and learn how to use it safely.
AR Annotations To Improve Device Design
AR can be used to create real-time digital mockups (digital twins) that can help detect and resolve medical device design and compatibility issues. For instance, you can check out a new device’s digital twin, share your findings with key team members, annotate concerns, or suggest alternative design concepts for better and more effective medical equipment.
Medical Equipment Marketing
AR-based demonstrations, simulations, and digital prototypes provide sales representatives with innovative ways to showcase the usage and benefits of new medical equipment and devices. With AR-based instruction manuals and videos, healthcare providers can see and understand how the new device works and supports their medical staff in a specific scenario, learn effective maintenance tips to extend the device’s life and performance, and know the best practices to optimize its usage.
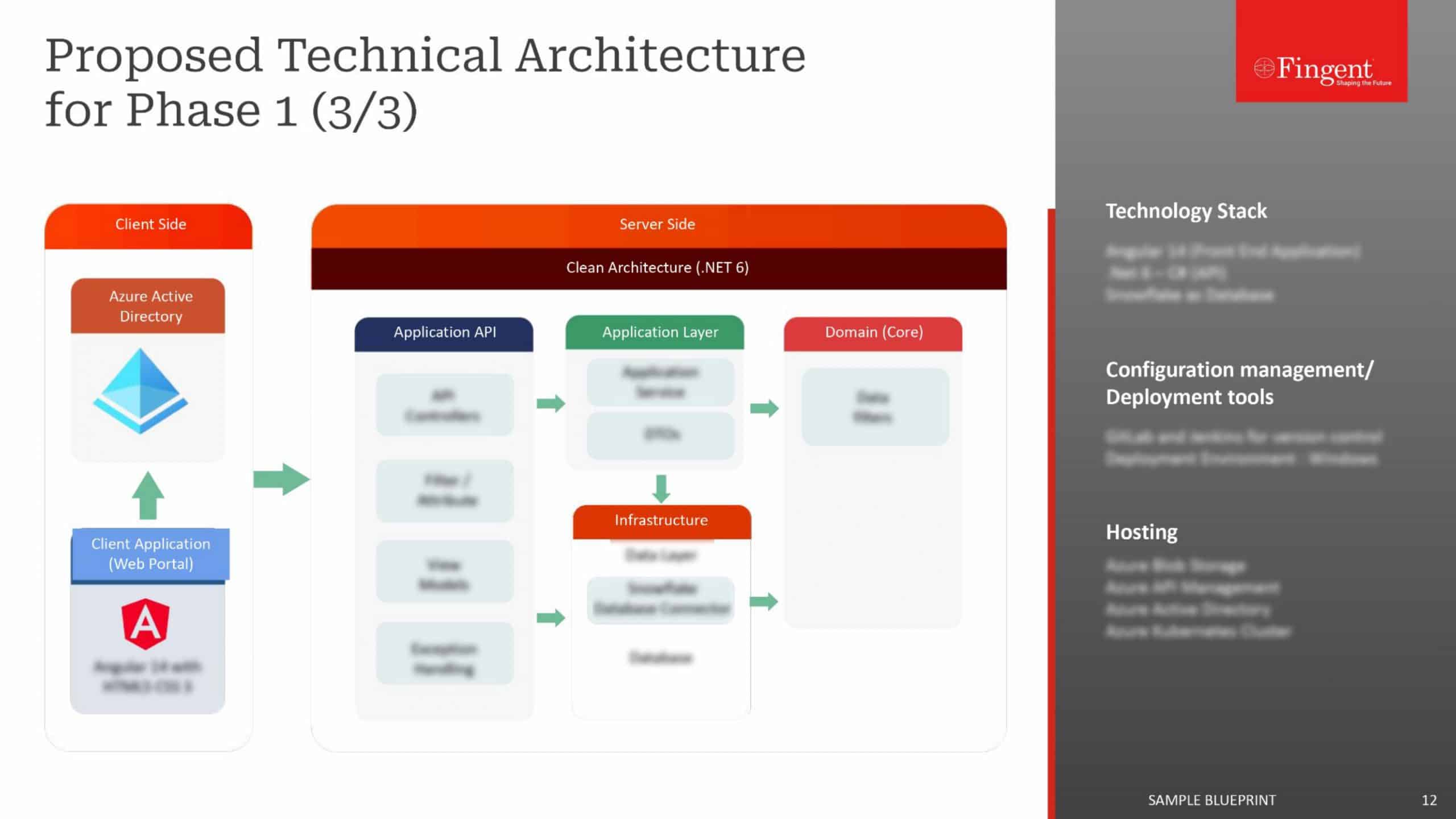
The Architecture of an Augmented Reality Solution
The architecture of augmented reality services typically involves the essential components that work together to deliver an immersive and interactive AR experience. Here is an overview of the critical components of an AR solution architecture:
The user interface component presents the AR content to the user. This can be achieved through various devices such as AR-enabled intelligent glasses, smartphones, tablets, wearables, or headsets. The UI component displays the augmented view, overlays digital content onto the real-world environment, and provides interactive elements for user input.
Using video tracking and mapping components, AR helps track and map objects correctly in the real-world environment. For instance, AR uses sensors, cameras, and computer vision algorithms to track the position and orientation of the physical object or device in order to create its exact virtual replica in real-time. Video tracking in AR maps the physical environment by identifying surfaces, objects, or markers as reference points for anchoring the virtual content.
The content rendering component of AR generates the virtual content to be overlaid on top of a physical object or device in real-time. Content rendering includes 3D models, animations, text, images, or videos that are rendered and aligned with real-world objects or locations. This component relies on the tracking and mapping information to ensure proper alignment, accuracy, and approach of the virtual content.
The content management component handles the organization, storage, and retrieval of AR content. It includes a database or content management system that stores and manages the 3D models, textures, animations, and other digital assets used in the AR experience. This component ensures efficient content delivery and enables dynamic updates or customization of the AR content.
AR solutions often integrate with various sensors to enhance the user experience by capturing real-time data, location, and positioning of physical devices. These sensors can include cameras, depth sensors, accelerometers, gyroscopes, or GPS receivers. Sensor integration allows the AR system to gather real-time data about the user’s surroundings, movements, or interactions, enabling more accurate tracking, object recognition, or environmental understanding.
For collaborative assistance or remote AR experiences, networking and communication components such as Wi-Fi, 5G, Bluetooth, and low latency internet connectivity are required to facilitate seamless data exchange between multiple AR devices or between AR devices and remote servers. This enables real-time collaboration and remote assistance for equipment maintenance tasks through effective sharing of AR content.
The analytics and performance monitoring component collects data about AR system usage, performance, and user interactions. It helps monitor the AR experience, gather usage statistics, and identify areas for improvement. This component may involve logging user interactions, tracking performance metrics, or capturing user feedback that go a long way in supporting equipment servicing and maintenance.
To leverage additional functionality or data, AR software needs to be integrated with the backend services of a business. This can include integration with enterprise systems, maintenance databases, IoT platforms, or cloud services. Backend integration of AR technology with business management platforms will enable real-time data synchronization, provide access to relevant information, and help augment existing workflows and processes.
All these components are required to create a seamless, immersive, and interactive AR experience by merging the real-world environment with the virtual world. The architecture may vary depending on the specific AR solution, platform, or hardware used, but these key components form the foundation of most AR systems.
Technology Elements Required for AR Software
AR Technology Over Years
- First generation: Technology to create images of real-world environments
- Second generation: Technology that allows the overlaying of 3D images over the images of the real-world objectsto create images of real-world environments
- Third generation: Technology that allows users to interact and engage with the simulated environments
Types of AR Applications/ Devices Commonly Used Today
- Mobile-Based AR
- Head-Mounted Gear AR (AR Headsets)
- Smart Glasses AR (Wearable AR)
- Web-Based AR
Technology Stack for AR Software Development
- Frameworks and SDKs for AR software development: Google ARCore, Apple ARKit, Vuforia Studio, Spark AR Studio, Unity3D
- 3D Modeling Tools: Maya, Adobe Dimension, Autodesk 3ds Max, Blender, ZBrush
- Image Recognition Software: OpenCV, TensorFlow, Keras, Caffe, SimpleCV, Google Colab
- Back-End Programming Languages: .NET, Python, Java, Golang (Go), node.js, PHP
- Cloud Data Storage: Cloud SQL by Google, Azure Cosmos DB, IBM DB2, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon Redshift, MongoDB Atlas
Technology Components of AR
- Artificial Intelligence: Most Augmented Reality solutions need artificial intelligence (AI) to work. AI helps process information for your AR application. For instance, AI can be used to allow users to complete actions through voice prompts.
- AR Software: AR software includes the tools and applications used to access Augmented Reality. Companies like Fingent help businesses create their own customized AR software.
- Processing: Processing power is required for your AR technology to work. It’s generally gained by leveraging your device’s internal operating system and hardware capabilities.
- Lenses: A lens or an image platform is required to view your AR content or images. The better quality your screen is, the more realistic your image will appear.
- Sensors: AR systems need to digest data about their environment to align the real and digital worlds. The information captured by your camera from sensors is sent through the AR software for processing.
Challenges in Implementing Augmented Reality
Potential limitations of using AR for equipment maintenance
- Ensuring the availability of compatible and reliable devices, software, low latency network connectivity, and accurate and updated data and content.
- Lack of design improvements in Head Worn Displays (HWDs) could potentially limit a user’s awareness of obstacles and other dangers, especially in maintenance jobs.
- User acceptance and adoption of a new way of working and learning can be difficult.
- Privacy, security, ethics or trust issues when accessing or sharing sensitive data or personal information.
- Organizational and cultural changes such as new policies, procedures, roles and responsibilities might be resisted or opposed by some stakeholders.
- Collaboration and coordination among different teams, departments or partners can also be a challenge.
- The main inhibitors of AR application for job aiding are lack of sufficiently capable head-worn displays, registration errors, risk of rejection, data integration, complexity, and value modeling.
Overcoming the challenges of using AR for equipment maintenance
- Analyze your needs, goals, business objectives, user expectations, equipment specifications and requirements, and organization-level expectations.
- Choose the right combination of devices, software, and platforms that can meet the specific requirements of each factor mentioned above.
- An AR application should employ registration error management techniques to allow the system to function properly even in the presence of errors.
- Provide your users (maintenance personnel) with adequate training and support, and feedback, so they can learn and use AR with improved confidence.
- Establish clear standards, guidelines, and protocols for using, creating, or sharing data and content (data governance).
- Implement adequate and robust security measures and management policies to ensure compliance with industry, organizational, and governmental regulations.
- Engage all the relevant stakeholders in the design, development, and evaluation of AR solutions to foster a culture of collaboration and innovation.
How Fingent Helps with Custom-Built AR Solutions
Fingent helps small and medium businesses as well large enterprises to accelerate their maintenance and repair activities through industry-specific, customized augmented reality technology solutions such as mobile AR apps and web AR software.
According to Research and Markets, the global AR market for Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul is estimated to reach USD 3,319.0 million by 2024. The market growth, accelerated by industrial and commercial channels, especially aerospace, automobile, and manufacturing segments motivate our experts to ideate and develop customized, industry-specific augmented reality software solutions and digital infrastructure for our clients.
Fingent is a top custom software development company that offers Augmented Reality consulting, development, implementation, continuous support and evolution of AR software, and a host of services tailored to your business needs. Contact our team to understand how AR adoption helps ensure continued productivity and profitability for your business.




 US
US Insurance
Insurance