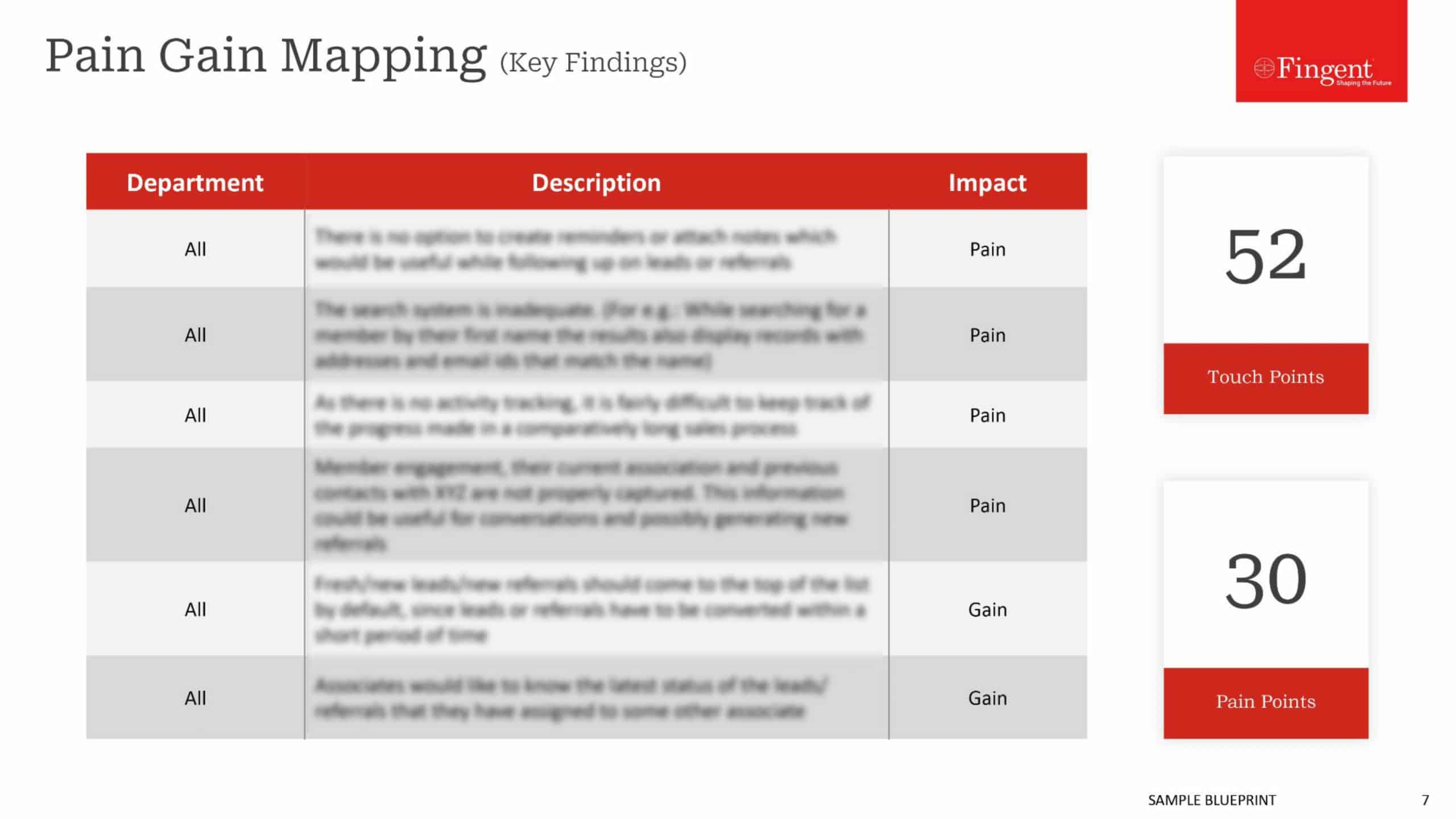
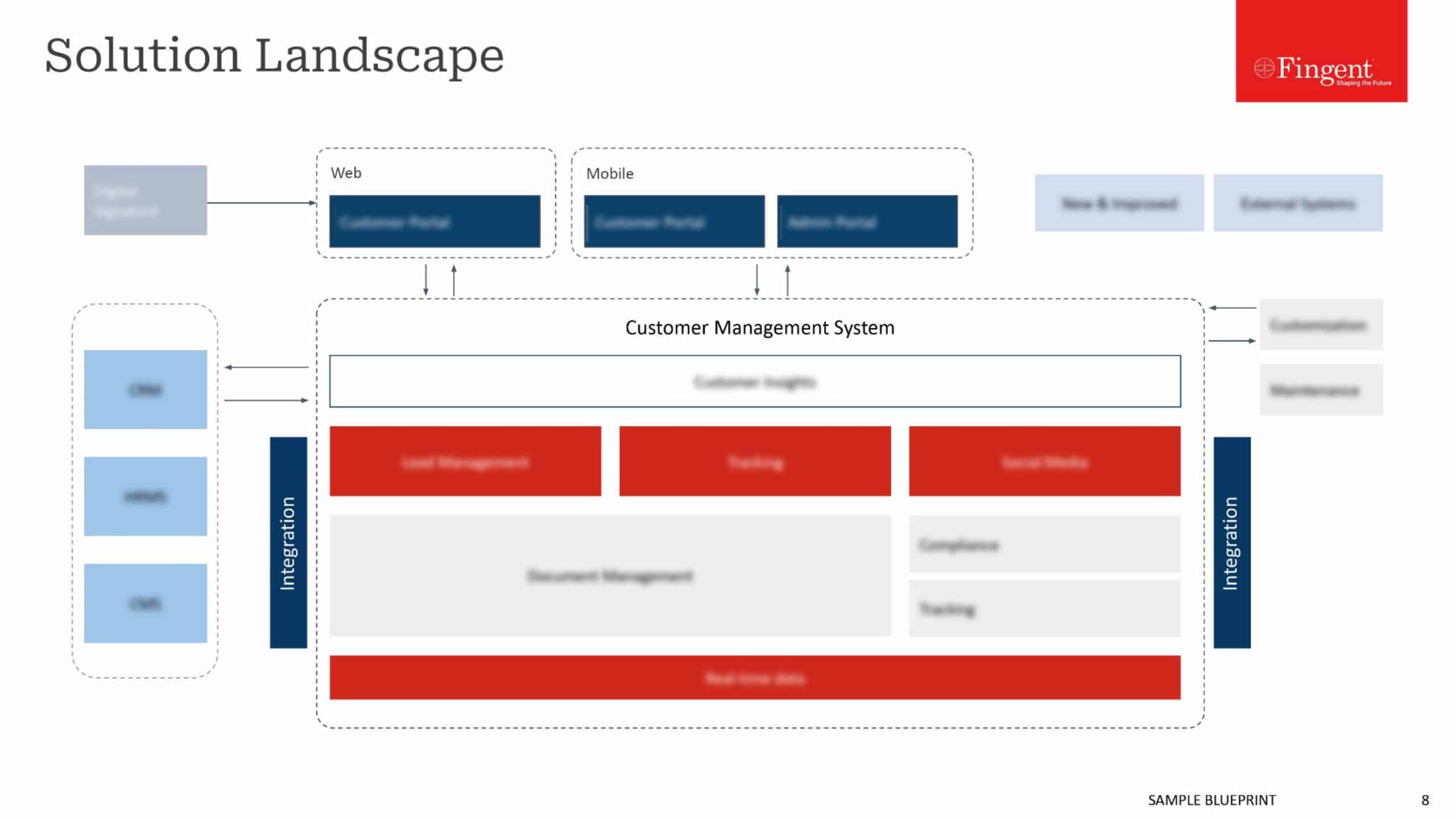
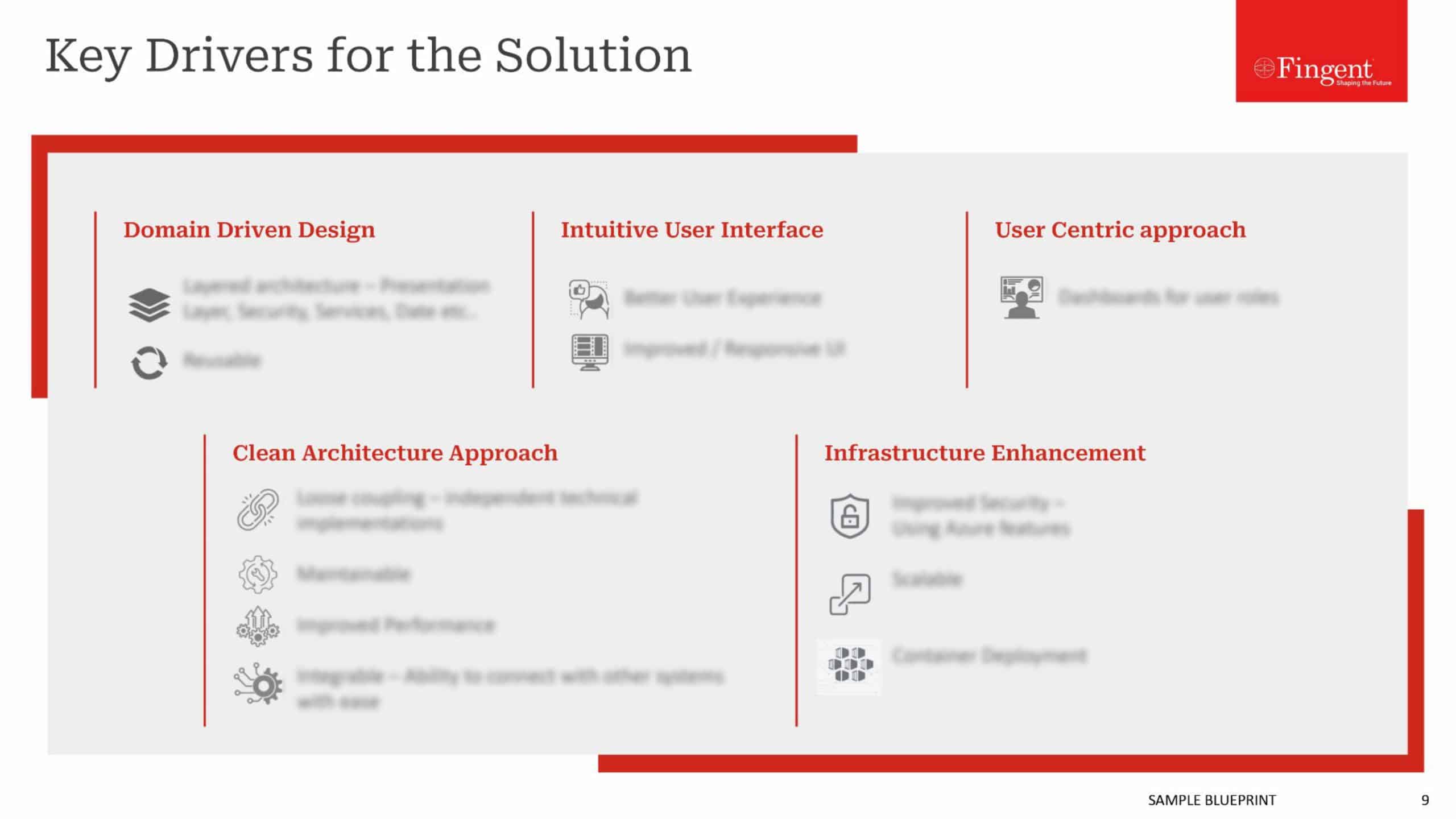
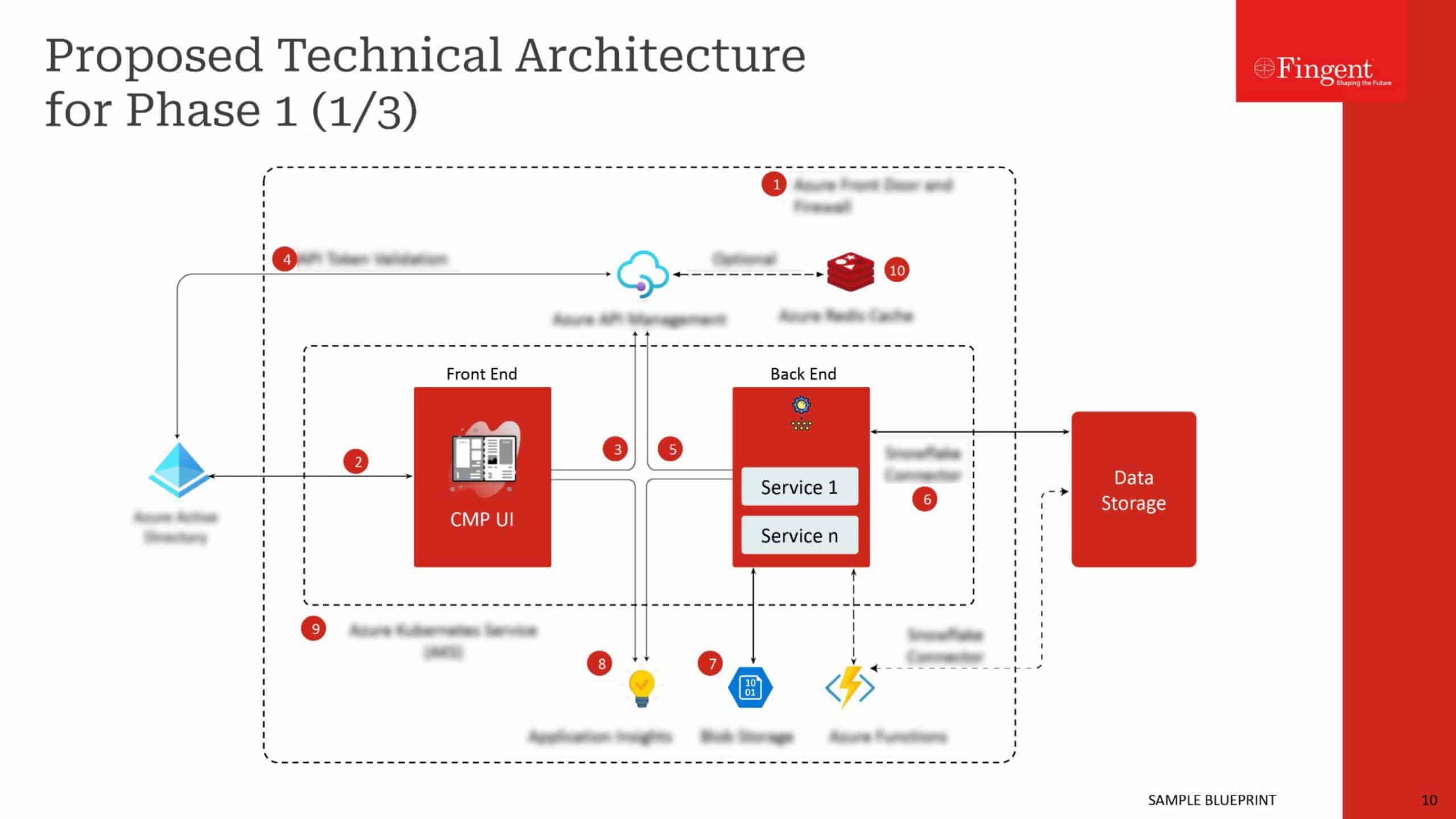
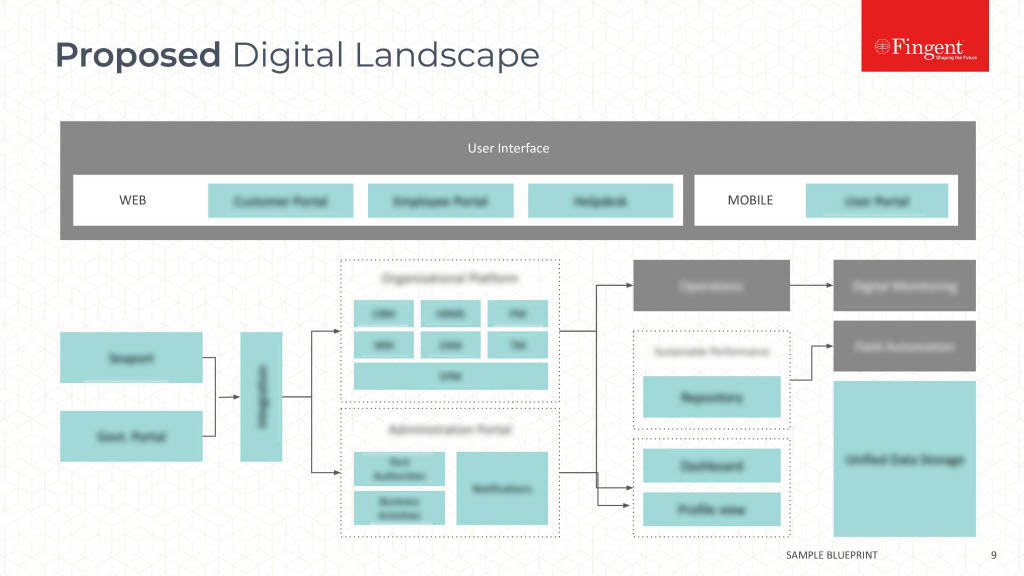
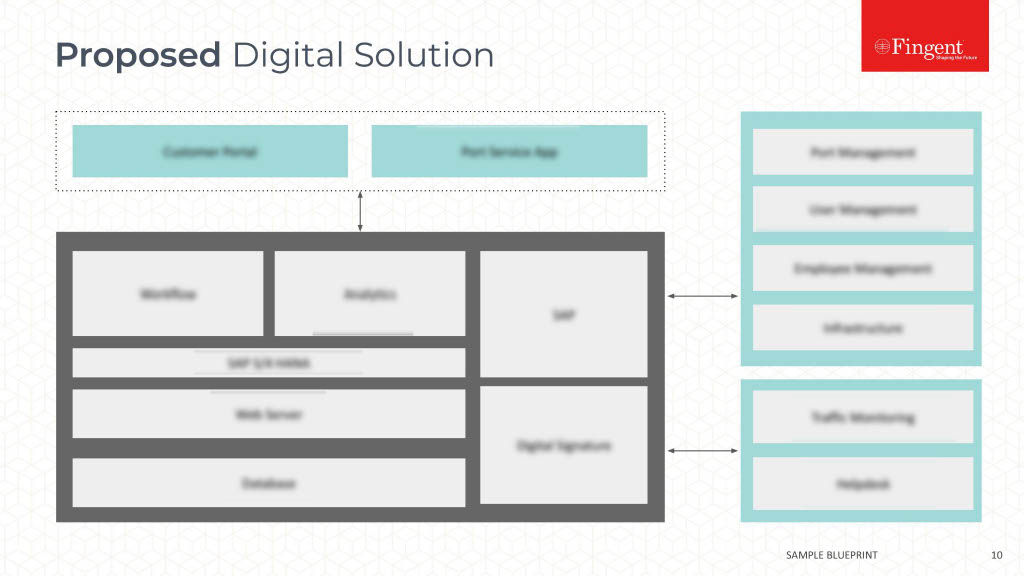
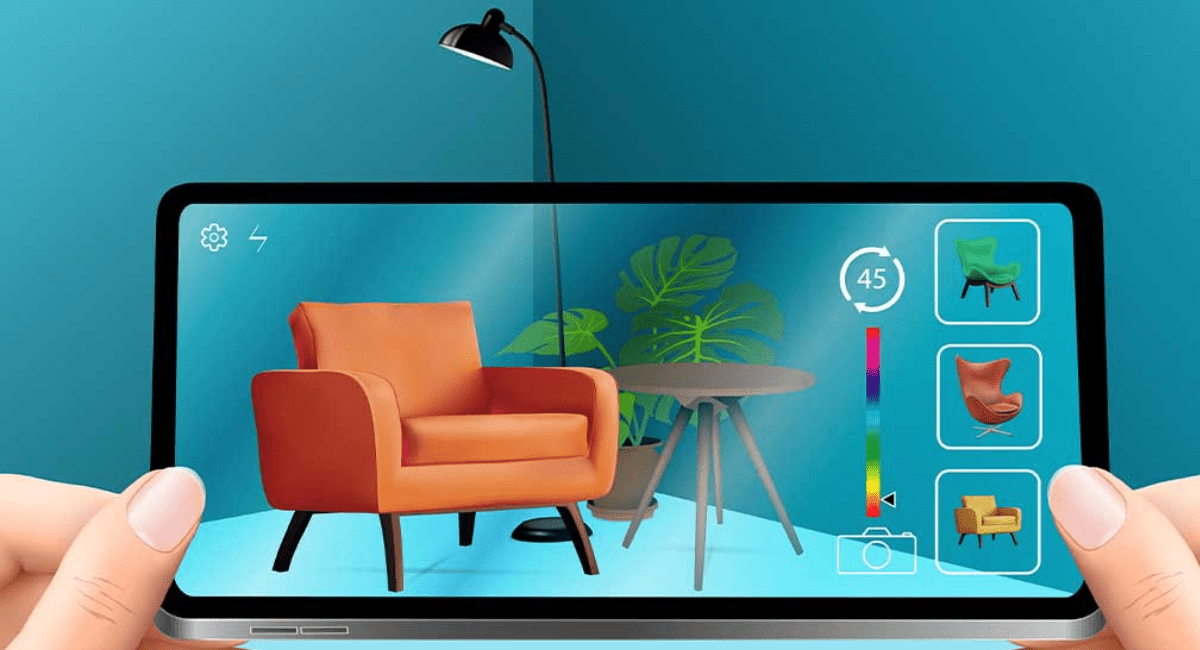
It’s no joke or a mere sci-fi theory! We’re experiencing the impact of Augmented Reality in healthcare, right in front of us. Using an AR-enabled head-mounted device, a surgeon can review patient vitals during a medical procedure without juggling multiple devices or displays. In doing so, they are less likely to misread or misinterpret the data.
Head-mounted displays, wearables, and mobile apps drive interactions between the physical world and virtual objects to improve the quality of healthcare delivery and patient experience. Just like how AI and data analytics improve your caregiving organization’s day-to-day operations, AR presents valuable opportunities for healthcare professionals and providers, payers, medical devices, and other players in the healthcare ecosystem. If you are looking forward to enhancing your healthcare organization’s performance, operations, user experience, and profits, you cannot bypass AR. All things considered, who wouldn’t like to augment their existing business processes instead of spending heavily on enabling new processes?
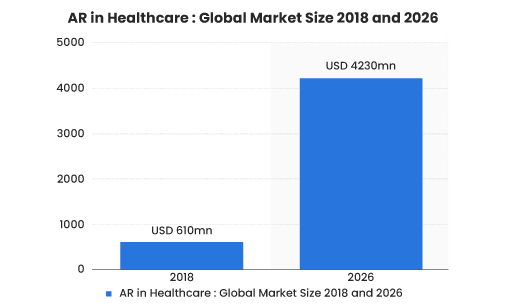
Data Source: Statista
According to ResearchAndMarkets, the global AR market will generate $152 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 36%, whereas the global AR healthcare market is expected to register a CAGR of 26% during the forecast period (2022-2027).
How Is Augmented Reality Creating An Impact In Healthcare?
Augmented Reality (AR) allows us to experience the real-life environment around us with a digital augmentation overlaid on it. AR works by integrating digital information or content into the user’s environment in real-time. In AR, the objects that reside in the real-world are enhanced using computer-generated capabilities. AR includes graphics, effects, sounds, text, and touch feedback to improve the user experience. In this technology, the user interacts with virtual objects placed in the real world.
Three essential components of AR include:
- Integration of real and virtual worlds
- Interaction with the objects in real-time
- Registration in 3D (The process by which AR applications can obtain a reference spatial framework to place the virtual objects so that they match the expected location with respect to the real ones.)
Due to its versatility, AR is becoming more accessible and affordable for medical imaging, medical education, dentistry, and nurses’ training.
The Most Impactful AR Trends in Healthcare Today
These ground-breaking AR trends in healthcare are expected to act as a magical boon that will help healthcare professionals overcome several medical limitations.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery (RAS) systems are gaining popularity in recent times as they improve surgical precision and dexterity, and provide better access to minimally-invasive procedures. Combining robotic-assisted surgery with AR offers an advanced interface which will enhance user perception. The ability of AR to improve situational awareness will tremendously advance the surgeon’s ability to make better decisions, in real-time. Robotic hepatic surgery, intraoperative reconstructions and tracking systems, robotic liver resections, preoperative imaging and 3D rendering, intra-operative robotic ultrasound application, etc. are some of the RAS fields which will be transformed by AR in the coming years.
The traditional methods used to assess wound parameters are mostly inaccurate, rough, and painful for the patient. Augmented Reality enables non-invasive assessment of wound parameters by providing visual feedback on the wound healing status. An accurate 3D model of the wound integrates AR functionalities based on a miniaturized projector to demonstrate wound progression. The availability of objective patient data allows doctors to suggest the right follow-up therapies and exercises. It also enables nurses to dress the wound properly. AR-based wound healing assessment offers patients a better understanding of their ailment, so their compliance to the doctor’s advice will improve significantly.
The healthcare industry is slowly realizing the game-changing benefits of AR in physiotherapy and behavioral treatment. Using AR in physiotherapy sessions increases patient engagement and improves physical outcomes. The data gathered from each session allows the physiotherapist to evaluate the outcomes better. AR makes way for a new, unobtrusive method of intervention in motor and cognitive rehabilitation by offering a safe environment for patients to practice movements and orient their exercises. It leads to greater patient motivation and enables caregivers to provide low-cost physiotherapy at home.
AR technology is an efficient time-saver that allows doctors to access patient charts from the EMR system and project the details in their area of vision, while attending a patient. AR glasses and interactive AR charts free doctors and nurses from thumbing reams of papers and documentation. Cloud-based data storage ensures that patient records are never misplaced, misfiled, damaged, or lost. Physicians can simply scan a patient’s hospital wristband and view the entire patient history which is retrieved by AR from the EMR database. It leads to a more meaningful patient-doctor relationship and saves the time taken for diagnosis and decision-making.
Multiple floors and buildings as well as insufficient maps or signage in large hospital facilities make indoor and outdoor wayfinding complex for patients, visitors, and entry-level medical trainees. Development of calibrated smartphone cameras and recent advances in computer graphics algorithms help simplify complex AR experiences in a larger environment, such as a multi-storeyed building. Using the patient’s phone camera, AR places virtual arrows on top of the images of their actual surroundings in real-time, enabling patients to navigate medical facilities with ease. Patients can effortlessly orient themselves in a hospital building and quickly reach their desired location by taking the shortest route.
Popular Uses of AR in Healthcare Today
- Accurate vein detection to draw blood
- Retrieve patient records faster
- Enable easy viewing of EMRs
- Simplify medical jargon for patients
- Assist surgeons during operations
- Guide medical practitioners to dress wounds
Fingent’s AR team develops customized AR applications to improve the quality of your HCO’s service and care, cut costs, and address your business requirements in the most efficient way. Connect with our team to learn more.
7 Real-Life Applications and Examples of AR in Healthcare
From medical training to patient care, diagnosis, monitoring, and other practical uses, AR is well-equipped to transform the healthcare industry. Here are some of the top applications of AR in healthcare:
1. Immersive and Interactive Medical Training
The Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) reports that the United States could see an estimated shortage of 124,000 physicians by 2034, including shortfalls in both primary and specialty care. AR-enabled virtualized training provides deeper insights into the nuances of body functions, enabling medical practitioners to address more critical cases in a given period of time.
FlexAR offers medical students a tangible, AR-powered anatomy learning experience using a prototype tool. The app gives users both written and 3D visual information about anatomy without the need for traditional study materials and cadaver dissections. Ohio-based Case Western Reserve University uses Microsoft HoloLens devices to study human anatomy where an entire class can view the same life-sized 3D image at once.
2. Training Physicians on New Therapies
Life sciences companies can use AR to educate care providers on the latest therapies and drugs that improve treatment outcomes. Companies can create compelling illustrations depicting the impacts of a disease or a virus on the human body at different stages and virtually demonstrate how the situation can be brought under control through novel treatment procedures, therapies, and drugs.
Application of Augmented Reality enhances the collaboration between the pharmaceutical community and doctors. The information collected by doctors using AR-based data visualization tools enable medical R&D teams to expedite the study of genetic data related to specific microbes. This paces up the discovery of drugs that can effectively combat the microbes. VisMol system, developed by Sygnature Discovery, uses Microsoft HoloLens technology to create an AR world that facilitates drug discovery collaboration.
3. Virtualizing Surgeries
Surgeons can leverage AR to create digital models of complicated surgeries that include multiple sub-steps and critical deviations requiring careful analysis and planning. The digital model of an entire surgery process details every step of the operation, allowing surgeons to optimize the sequence based on in-depth virtual analysis. As a result, surgeons will be better prepared to handle contingencies and lay out the course of action in advance, before entering the operating suite.
xvision Spine System developed by Augmedics (Chicago, IL), is a cutting-edge AR surgical guidance system that allows surgeons to “see” the patient’s anatomy through skin and tissue just like how they view X-rays. The X-ray like vision allows surgeons to accurately navigate instruments and implants during spine procedures.
4. Accurate Symptom Detection
Several patients find it challenging to explain their current health conditions to doctors. Some patients may exaggerate their symptoms, while others share only minimal information. This could result in incorrect diagnosis and wrong therapy. AR solves this problem by offering patients a simple and handy way to check their symptoms and current health status all by themselves. Doctors can also analyze the health reports projected by AR and suggest accurate remedies and lifestyle improvement therapies to help the patient stay fit and healthy.
EyeDecide AR app uses a camera display to simulate a patient’s eye anatomy, conditions, and solutions. The app describes each condition, annotates symptoms and findings adjacent to each medical image, and suggests treatment based on best practices. This allows the doctor to examine the symptoms precisely. The patient is also spared from any kind of communication challenge.
5. Patient Self-care
AR-enabled healthcare software solutions allows patients to become proactive in their own care. Physiotherapy and physical rehabilitation are two of the self-care areas where AR can be highly beneficial. By watching AR-based digital demonstrations of their bodily motions and actions, patients can refine their movements to restore physical fitness. Patients can also point their smartphone camera towards a city landscape to find information about nearby hospitals and get the direction to reach their destination.
Know My Heart and Know My Beat are two of the leading patient self-care apps designed specifically to use AR technology. The first app enables an individual patient to self-check their pulse and detect possible AF (Atrial Fibrillation). The second app aims to educate patients who have been diagnosed with AF to be more aware of their health condition so that they adhere to the prescribed medication and seek timely medical aid, when required.
6. Vein Visualization
Injecting intravenous shots or collecting blood samples for medical tests is a painful and unpleasant experience for many patients, particularly if the patient’s vein is missed in the first instance. Thanks to AR handheld scanner technology and near-infrared imaging, a nurse can easily see the vein to take blood or give a jab. The handheld scanner projects veins over the skin to prevent injection failures in patients and improve the first injection success ratio.
AccuVein’s vein finder uses AR technology to find a patient’s vein at the very first try of an IV start or a blood draw. The vein finder is a portable handheld device supported by a digital laser projection, a laser-based scanner, and a processing system. Projection-based AR allows the user to view a real-time virtual image of the underlying vasculature on top of the skin. Using AR for vein visualization has helped improve the first-time vein detection success rate by 3.5 times.
7. Medical Imaging
AR displays in operating rooms leverage sophisticated algorithms to convert CT imaging (Computed Tomography scan) into a dense 3D map of structures. Based on the surgical procedure’s requirements, this 3D map can be displayed on a nearby screen, through a headset, or projected onto the patient. Thus, AR technology provides surgeons an enhanced surgical field to sketch a detailed operating plan, well ahead of the first incision. Similarly, arteries and tumor structures can be superimposed into an operating field display to enable more accurate real-time viewing of underlying tissues, organ motions, and deformations.
Immersive Touch’s image-guided AR platform provides surgeons with 3D holographic “X-Ray vision” through the skin that visualizes patient specific anatomy intra-operatively. It aims to offer detailed anatomical data of the patient at various surgical phases. The platform helps surgeons navigate their instruments accurately without losing sight of the patient.
Watch Video: How AR can be a powerful learning tool in the future

Practical Use Cases of AR in Healthcare
AR in Bioinformatics
AR in Pharmaceutical Marketing
AR-based Telemedicine
AR-aided Collaborative Surgeries
AR in Prenatal, Neonatal, and Postnatal Care
AR in Bioinformatics
Augmented Reality can complement traditional visualization techniques which will create a major breakthrough in the field of structural bioinformatics. AR can be used to develop highly understandable and impactful 3D visualizations of complex biomolecules. The widespread popularity of mobile devices helps extend AR to the end-user in a simple and inexpensive way. Users can view the 3D visualization of biomolecules using their smartphones and interact with it in an AR environment. This increases student motivation and understanding and also simplifies data analysis in bioinformatics.
AR in Pharmaceutical Marketing
Soon AR will make “show, don’t tell” the new maxim in pharmaceutical marketing. By projecting 3D images and visualizations into what’s being viewed in the real-world, AR presents an incredible opportunity for pharma companies to virtually showcase their marketing materials to potential clients. For example, a customized AR software can be used to create a 3D model of the human heart to demonstrate how a particular drug functions and its effects post intake. This offers healthcare professionals deeper insights into the benefits of new pharma products and also helps them explain to their patients how a new treatment or medication will work.
AR-based Telemedicine
Custom healthcare AR applications are being developed to train medical students and lab assistants to successfully operate, assemble, disassemble, transport, and maintain complex medical devices or systems. One of the best examples of AR in telemedicine services is training unskilled users to perform ECG tests. Through interactive virtual simulations powered by AR, untrained users can interact with the ECG device and understand how to properly place ECG electrodes on a patient’s chest. Dearth of skilled service providers is a major obstacle in implementing telemedicine. We hope that AR could fill the gap soon.
AR-aided Collaborative Surgeries
When the chief surgeon is miles away and there is no specialist nearby to attend a critical patient, AR comes to the rescue. Collaborative surgeries, made possible through AR video conferencing, can be life-savers. Clinicians in possession of the right AR tools can collaborate with their colleagues who are located far away and receive instructions in real-time. Platforms like Proprio combine AR and machine learning to generate 3D medical images with extra precision, allowing medical experts located anywhere to team up, discuss surgical tactics, and perform the procedure successfully.
AR in Prenatal, Neonatal, and Postnatal Care
AR can be leveraged to offer expectant mothers and new moms a multisensory educational experience by visualizing how they need to care for themselves and their newborns. The Australian Breastfeeding Association utilizes AR to develop engaging tutorials featuring key concepts related to breastfeeding, such as guidance and counseling services for new moms, which boosts their confidence and alleviates postpartum blues. AR-based visualizations can replace the dreary literature in textbooks and provide a positive experience for new moms, which they will quickly understand and remember.
Future of Augmented Reality in healthcare
The increased use of smartphones and other mobile gadgets will augment AR-driven healthcare practices and service delivery in the future. Some of the most-awaited AR-led transformations in healthcare are listed here.
1. AR in Dental Practice
In recent times, AR is being employed in pre-clinical dental education and operative dentistry learning. From a clinical perspective, maxillofacial, orthognathic, oral, and implant surgeries will be increasingly aided by AR in the coming years. In endodontics procedures, video tools optimized using AR are being used to detect orifices for accessing root canals. AR also helps dentists to place brackets in orthodontics through 3D image-based tooth-tracking. The ability of AR to enhance spatial visual perception will go a long way in pre-clinical practices, such as designing treatment cavities for student analysis and learning.
2. AR for Psychomotor Skills Training
AR training tools facilitate spatial and psychomotor skills training in the medical domain. While interacting with virtual objects superimposed on physical environments, learners get real-time feedback leading to positive learning outcomes. An interactive AR hand hygiene training tool for healthcare workers developed by a team of researchers from Ireland and Scotland enabled 81% of participants in the pilot program to attain proficiency after two-minute practice sessions. In the coming years, AR will increase the scope of self-directed skills-based training, improving skill acquisition and retention.
3. AR to Gamify Workout Sessions
AR can lower healthcare costs considerably, save thousands of lives, and improve our standard of living drastically. Even if you are working out from home, you can livestream and workout with others digitally using AR apps like FitTech. Even a monotonous morning walk can be made more enjoyable using AR. Apps such as “Zombies, Run!” can gamify daily running tasks, motivating users to take care of their health more seriously. Medical imaging and diagnosis will be simplified, and dietitians and nutritionists can use the findings to encourage people to bring desirable changes to their lifestyles.
How Fingent Can Help You with AR Services
Fingent is a high-end custom software development company that helps businesses -small and large- across the globe with innovative solutions. We provide a wide array of software development services from software customization to building Web, Mobile, Enterprise, and Cloud applications across various industries.
Our team at Fingent helps you develop customized healthcare AR applications that improve the quality of your HCO’s service and care, cut costs, and address your business requirements in the most efficient way. Build your brand, increase your brand identity, promote your products and services, and gain a competitive advantage with our AR consulting, development, and implementation services.
Fingent’s custom AR services are garnished with:
- Transparent project management
- Specialized AR and VR teams
- Access to the latest, best-in-class technology
- Cross-industry experience
- Rapid turnaround time
- Smooth and successful engagement
Most Common Q&A on Augmented Reality in Healthcare
Augmented Reality is used to simplify various clinical practices such as operating suite preparation, accurate vein visualization on the patient’s arm for drawing blood, dental learning and practice, immersive medical training, 3D medical imaging, real-time access of patient data from EMRs, precise symptom detection, collaborative surgeries, and so on.
AR-based 3D visualizations and virtual simulations allow patients to understand their health conditions better. Increased awareness of self-health encourages patients to adhere to the medical advice given by their physicians. AR can convey clinicians the symptoms or conditions which their patients wouldn’t have revealed or struggled to explain. Using an AR-enabled head-mounted device, a surgeon can review patient vitals during a medical procedure without juggling multiple devices or displays. In doing so, they are less likely to misread or misinterpret the data. To keep it short, AR brings more transparency into patient care, boosts the productivity of doctors, nurses and health workers, and ultimately improves the quality of healthcare services and delivery.
Surgeons can leverage AR to create digital models of complicated surgeries that include multiple sub-steps and critical deviations requiring careful analysis and planning. xvision Spine System, for example, is a cutting-edge AR surgical guidance system that allows surgeons to “see” the patient’s anatomy through skin and tissue just like how they view X-rays. The X-ray-like vision allows surgeons to accurately navigate instruments and implants during spine procedures.
We help you deploy AR to improve medical training, pediatric MRI evaluation, medical imaging, venipuncture procedures, dentistry, remote surgical procedures, and more! Our team at Fingent delivers augmented reality services that can improve the quality of your HCO’s service and care, cut costs, and address your business requirements in the most efficient way.
Augmented Diagnosis is a process in which AR is employed to diagnose patient symptoms, medical imaging, and health vitals through 3D modeling and visualization. It improves doctor-patient communication and helps accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Augmented Practice is being used by medical training institutions and colleges to simulate surgical encounters and real-life patient conditions for students. It improves positive learning outcomes through enhanced skill acquisition and retention.
Augmented Surgery allows surgeons to understand their patient’s anatomy by digitally overlaying MRI data, CT scan, and health reports on top of their patient’s body. It offers surgeons an enhanced surgical field to sketch a detailed operating plan, well ahead of the first incision.
Although AR is perceived to have great potential in many industry sectors, its utilization is yet limited. This is mostly due to the many challenges businesses often face while adopting AR. Here are a few challenges to mainstream AR adoption listed:
- >> Users are still skeptical about the right uses and benefits of AR
- >> Cost constraints limit access to AR headsets and hardware
- >> Being intensely immersive, AR is often considered physically harmful
- >> Limitations in AR content creation for businesses
- >> Lack of regulations to govern the use of AR



 US
US Insurance
Insurance