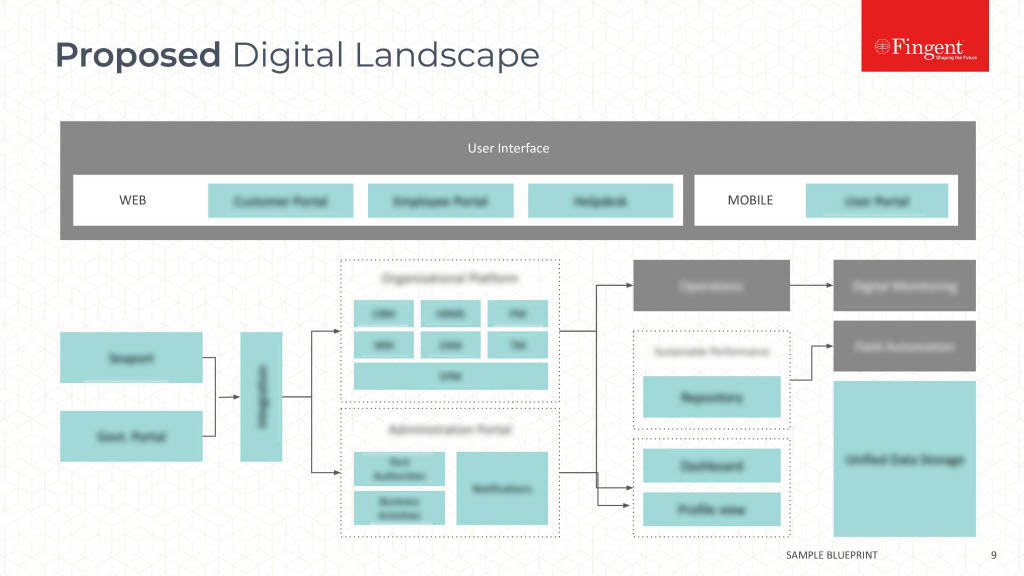
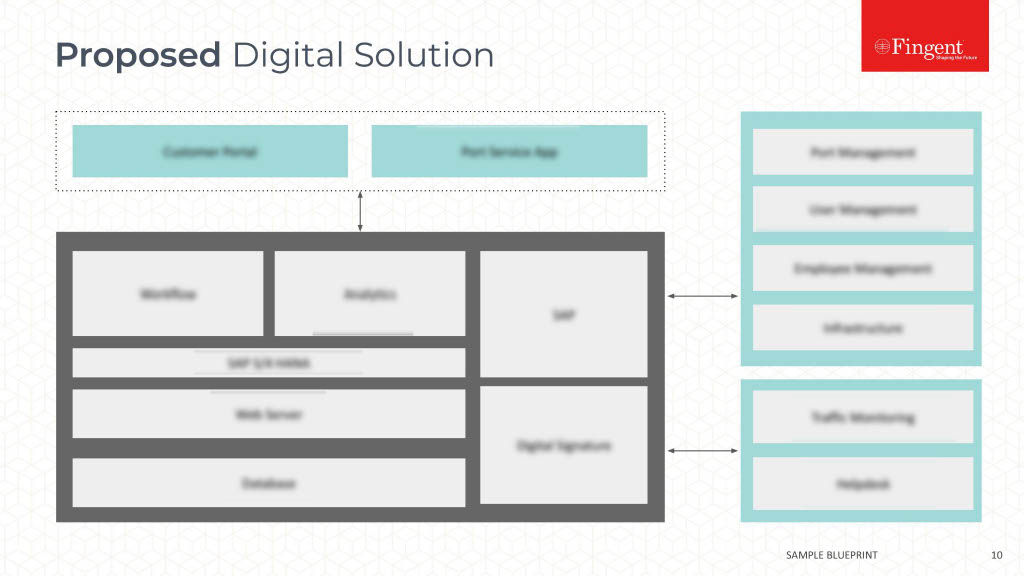
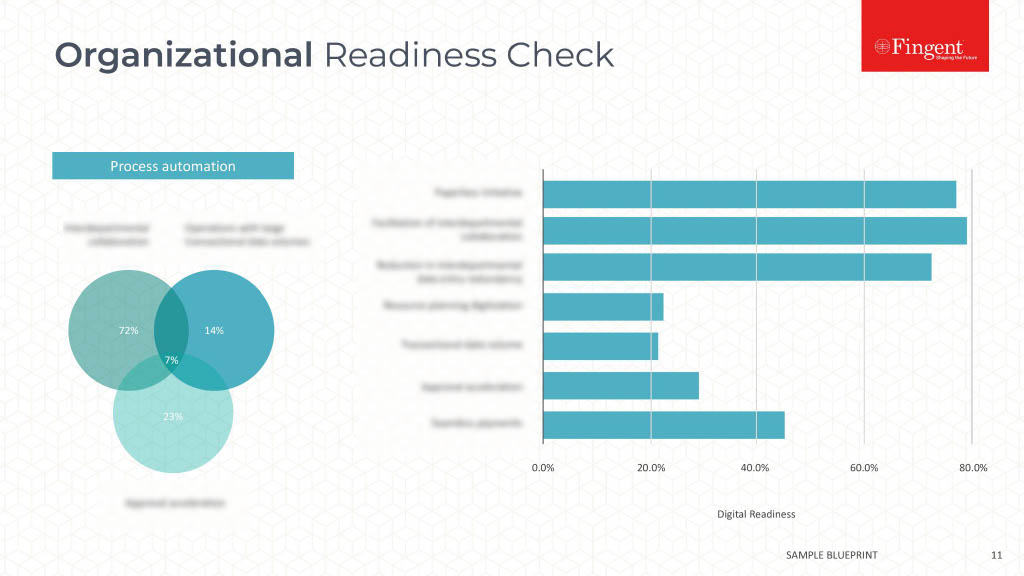
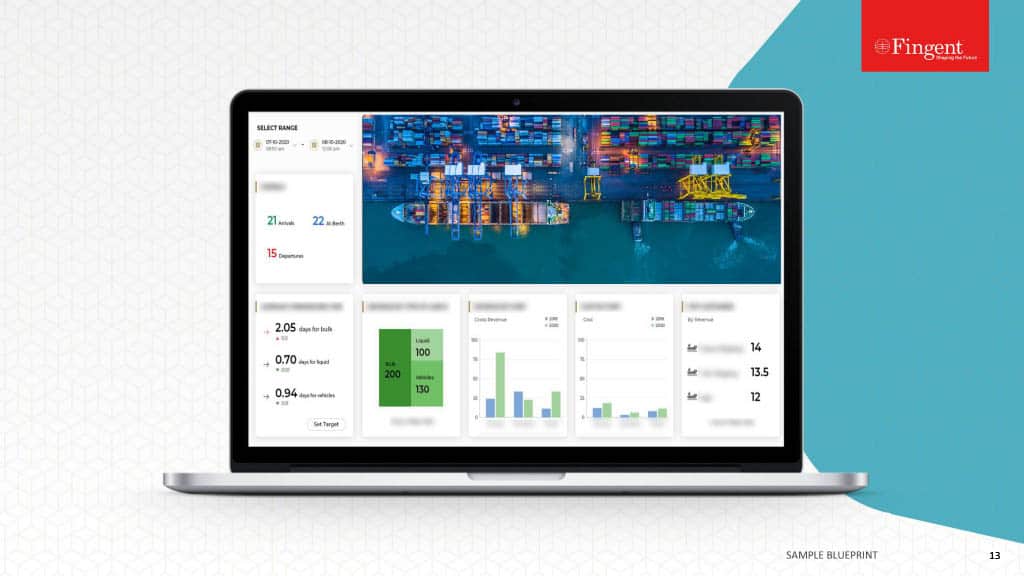
Why Choose SAP and How to Plan your Budget for it?
SAP, which stands for Systems, Applications and Products is an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system by SAP AG, world’s largest inter-enterprise software company based in Germany and the fourth-largest independent software supplier in the world. The basic idea of SAP was to enable employees/customers interact with a common corporate database for a broad range of applications used in companies. SAP applications have the ability to store, analyze, retrieve and process the enormous corporate data from production, operations, Human Resources, finance, distribution, and other business processes in the company. In 2015, SAP concentrates on five major market categories: Applications, Mobile, Analytics, Cloud and Database & Technology. SAP provides its products and services to more than 296,000 customers distributed in 190 countries that span small businesses to large multinational leaders, like IBM and Microsoft.
Why SAP?
- Medium sized companies face the challenge of limited resources (IT staffs, budget, and skills) and therefore, need to balance between appropriate levels of business value, functionality, support, and costs.
- Gartner forecasts that BI, performance management, and analytics will be widespread by 2020, unfortunately, midsize businesses are still struggling to go beyond fundamental reporting and analysis.
- With their very limited resources, midsized businesses will need an all-encompassing system that is affordable, easy and capable to support the company’s growth and efficacy.
- Increased adoption of mobile, Big Data (increases at over 40% every year), social networking and cloud computing in enterprises have all necessitated the need for change from the traditional technology stack being used in companies.
- Customers are seen to spend less on hardware and services, and are heading to software-based innovation, social or collaboration technologies in cloud.
SAP adapts all these changes and lessens the weaknesses, making people centric cloud applications that cross the traditional boundaries of enterprises. These enable ubiquitous mobile friendly scenarios that empower new business models in developed and emerging markets. These solutions help to increase visibility into the business via real time notifications, reporting etc., which in turn favors better planning and forecasting of processes. It allows businesses to streamline their business processes through proper standardization, better performance and provides deep insights into their business.
SAP has numerous “run your business” products, for example, SAP Business Suite that is an integrated and diverse set of software modules for running businesses of any size; SAP Business-All-in-One that is a packaged set of software modules pre-configured for small and medium sized businesses with about 450 employees; or SAP Business one, which is a software package for small businesses.
According to CMI analysis, the market opportunity of SAP Business All-in-one is expected to rise up to $65 billion worldwide in 2016, across all its five market categories. SAP Business All-in-One, for instance is a very strong solution that satisfy the requirements of medium sized companies by integrating with their core ERP and innovations (SAP HANA Live, Fiori, Mobile) combined with local expertise and industry best practices. It is an ‘all-inclusive’ solution for medium sized companies that will significantly reduce the need for add-ons, reducing the costs and complexities, and accelerating implementation. It has flexible deployment options to satisfy capital and operating structure needs that includes subscription based hosting and deployment to the cloud.
SAP Pricing
Let’s consider for example, SAP Business Suite, the installation of which primarily requires 2 license models that are offered separately: a software license and its associated maintenance and support services. The software license is paid at the time of purchase. These licenses are perpetual without restrictions. The license fee varies according to the modules installed and the hardware the company currently runs in. The support and maintenance services provided by SAP for its licensed software are done for a recurring fee.
SAP business solutions has base ERP foundation and can be extended with application extensions as required by the industry vertical or line of business processes that are to be supported. Licensed third party products from SAP are generally considered as SAP applications and the maintenance and support of such applications differs from the SAP maintenance and support mentioned in previous paragraph. Third party software license included as a part of SAP products are required to use these applications in association with SAP software.
SAP licenses its software through a combination of Named user licenses and Package licenses. SAP pricing therefore encompasses per application licensing costs and per user licensing costs. Now, Depending on the package being licensed, the application licensing costs can vary depending upon a number of factors like: Application Module, number of employees, number of orders, revenue, Master Data Objects, number of plants or locations, number of customers, flat fee, and number of Users. Any user using the licensed packages needs to have the appropriate Named User license with different costs and capabilities. For instance, the Named user license cost and permissions for a developer will be different from that of a service user.
SAP Business Suite then requires a licensed, SAP compatible database which can be obtained from SAP or other third party vendors (Oracle, Microsoft, etc.). The costs of these databases vary based on factors like its features, size, number of cores, number of current sessions, memory of server and number of users. It should be then configured according to the SAP applications deployed in the business, with necessary server memory, hardware availability and processing power capabilities.
How to calculate Contract Price?
1. Add the list prices of SAV relevant price list items to determine the SAV (SAP Application Value): SAV is determined separately for discounted and non-discounted price list items and excludes all non-SAV items.
2. Apply the correct percentage to SAV to calculate the Database price. Calculate the discounted and non-discounted part of the database price separately.
3. Determine list price for the non-SAV items (items that don’t contribute to the SAV): the list price subtotal for discountable and non-discountable non-SAV items is performed separately.
4. Determine the Total list price: The sum of above three values (which is the sum of discountable and non-discountable part of SAV, database price and the non-SAV value).
5. Based on this total list price, calculate the Standard volume discount percentage.
6. Calculate Contract Price: apply the above discount percentage to discountable part of the total list price and add this result to the non-discountable value of total list price.
For a mid-sized company offering services, having about 250 employees (~100 users), a SAP Business All-in-one solution can cost around $579,700 USD including the SAP software, implementation services and Hardware. This will include modules like, financial accounting, Controlling, Materials Management, Sales, Manufacturing, Research & Development, Services, and Cross Functions and Analytics. Each of these has its own sub-modules, for example, in the Financial Accounting module the submodules covered by SAP All-in-one solution are: General Ledger, Accounts Receivable, Accounts payable, Period end closing financial accounting and Asset accounting. Similarly, you can calculate the SAP All-in-one solution estimate for different industries of different size.
What we said above is just a rough estimate; generally the cost of the business management software you opt depends on how you deploy it, covering 5 major areas like: Deployment model (where you can pay upfront), Software Licensing (costs vary according to the number of users and access types required), Implementation (Cost varies according to business requirements), Hardware (depending on your current hardware, you may have to plan budget for upgrades or new equipment), and Maintenance: maintenance and support services, upgrades, new releases cost etc.
At Fingent, we have helped enterprises start, manage and master SAP and non-SAP solutions using solution manager platforms, to improve their operational efficiency and lessen the business challenges. If you wish to automate your IT processes with SAP services, and would like to know the detailed structure, costs of implementation or any related information about it, get advice from our SAP experts.
Image credits: 360b / Shutterstock.com
Stay up to date on what's new

Recommended Posts

21 Jan 2024 B2B
The Impact of SAP S/4HANA Cloud and BTP Collaboration on Business Transformation
In today's fast-paced business world, staying competitive goes beyond traditional strategies. The digital age requires a seamless blend of cutting-edge technologies. SAP, a global leader in enterprise software, offers a……

17 Dec 2023 B2B
What Is to Know About The New SAP S/4HANA Cloud 2111 Release
Which transformation path aligns with your business objectives? This is a critical question to ask when designing your business transformation journey. This makes it vital to take the time to……

15 Nov 2023 B2B
SAP S/4HANA Cloud Migration – All that You Need To Know!
“Our future success is directly proportional to our ability to understand, adopt and integrate new technology into our work.” – Sukant Ratnakar – CEO, Quantraz Inc. Since the dawn of its……
23 Aug 2023 Logistics B2B
SAP Transportation Management: A Comprehensive Overview
SAP software, as most of us know, is a tool used to control all aspects of critical business functions specifically. It integrates and automates key processes, ultimately helping organizations run……
Featured Blogs
Stay up to date on
what's new













 US
US Insurance
Insurance