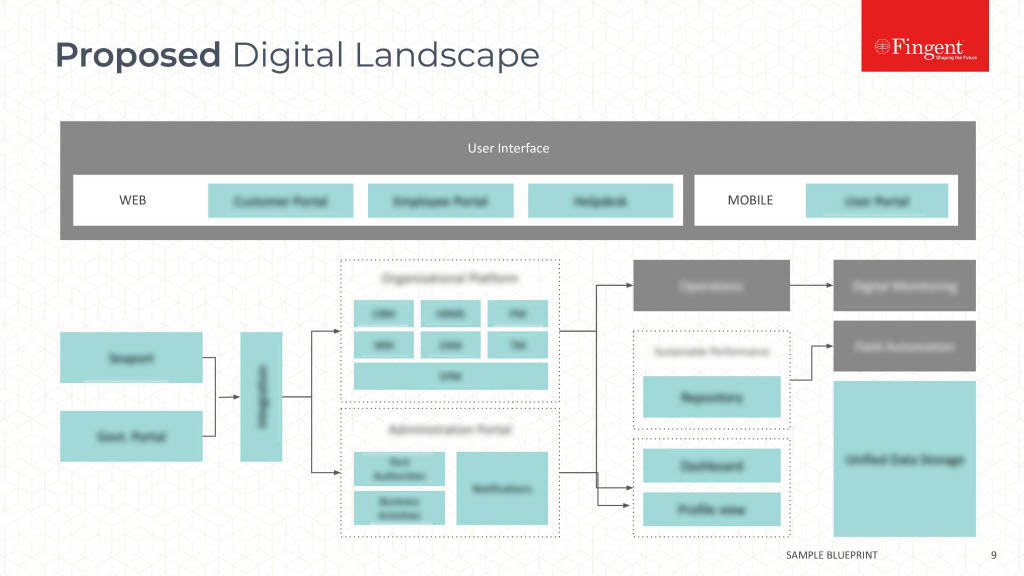
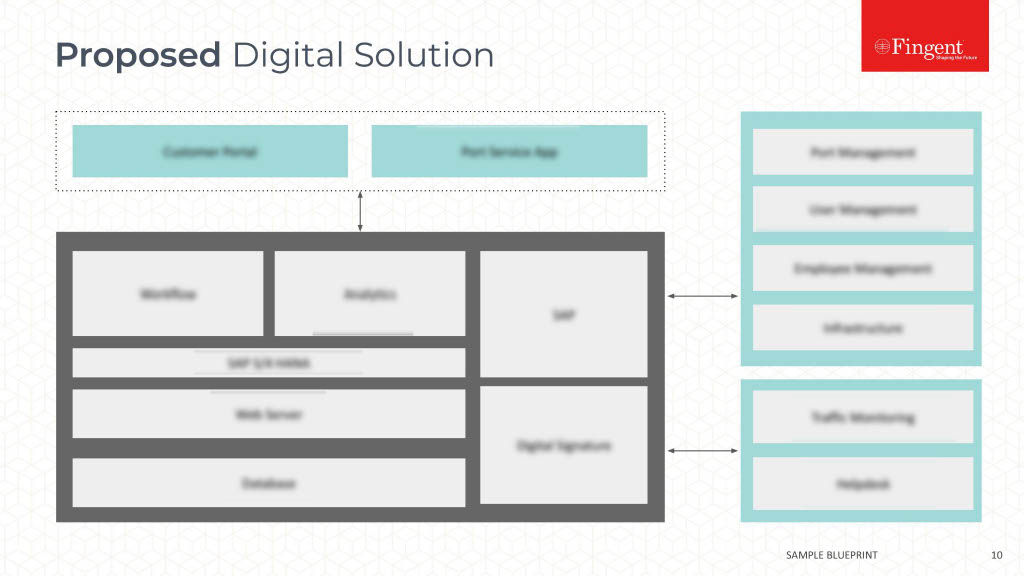
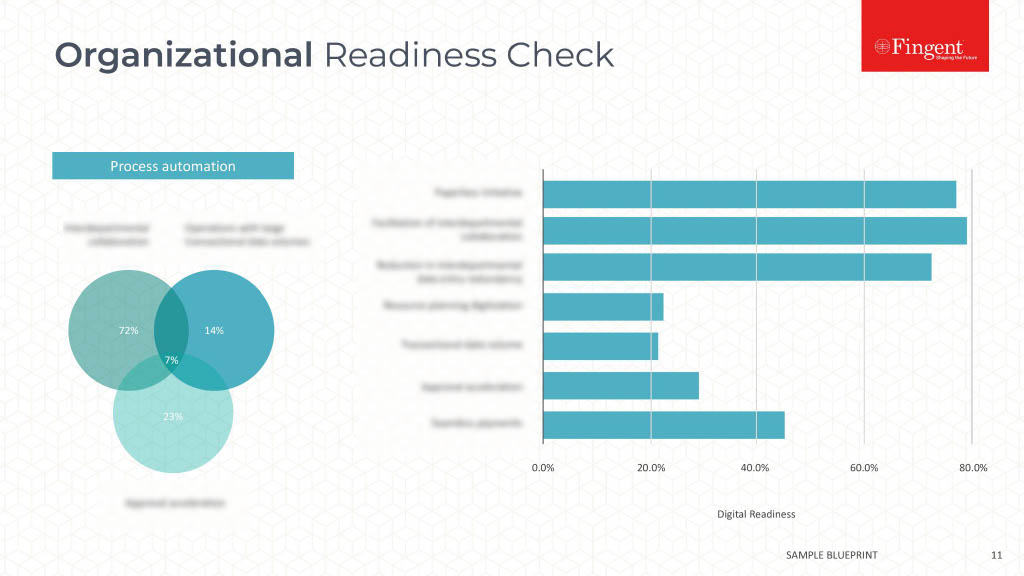
Making a Choice
How to choose the right cloud computing service model?
Three cloud computing service models for your business:
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
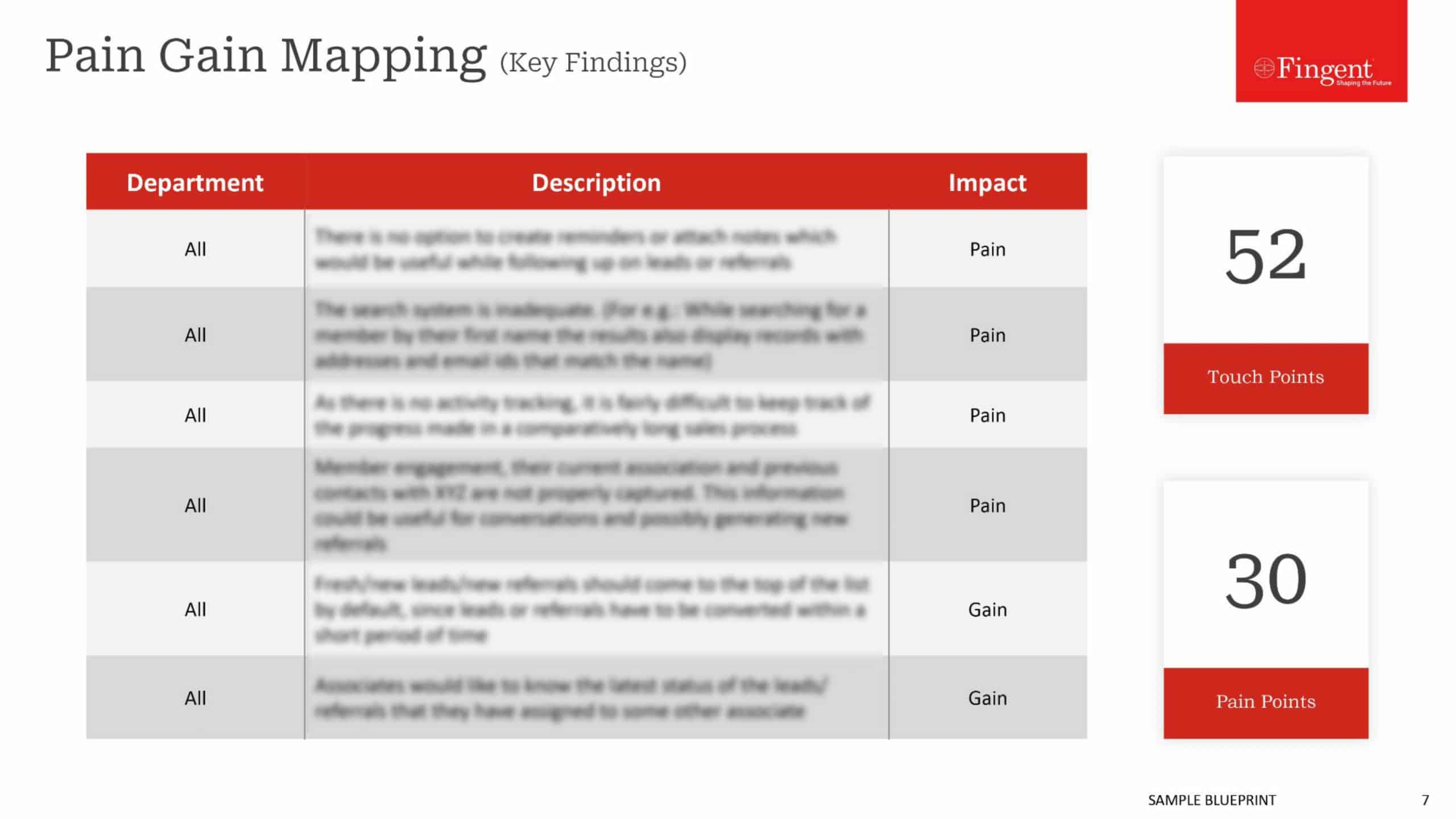
| SaaS | IaaS | PaaS | |
| Managed by you | – | Software data and apps, platform OS, runtime, and middleware | Software (hosted applications) |
| Managed by your vendor | Everything related to your software, infrastructure, and platform | Infrastructure management (servers, storage, networking and data center) | Infrastructure and platform development and management |
| Managed by you | Managed by your vendor | |
|---|---|---|
| SaaS | – | Everything related to your software, infrastructure, and platform |
| IaaS | Software data and apps, platform OS, runtime, and middleware | Infrastructure management (servers, storage, networking and data center) |
| PaaS | Software (hosted applications) | Infrastructure and platform development and management |
Software as a Service (SaaS) fits organizations that want to:
- Benefit from application usage without the need to maintain and update infrastructure and components
- Don’t want to reinstall applications or purchase new licenses each time when switching to a new device
- Cut down on internal IT overhead and retain only the subscription cost of the SaaS application
- Gain more compute power and database storage depending on the usage
- Great deal of flexibility to operate from any device, any location, any time
- Receive ongoing application upgrades with less customer risk and lower adoption cost
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) fits organizations that want to:
- Consolidate heterogeneous disaster recovery systems into one virtualized environment
- Perform big data analysis that requires a lot of processing power
- Manage unexpected traffic spikes by scaling on-demand
- Get new projects up and running quickly, according to changing business priorities
- Overcome application performance limitations caused by capacity constraints
- Experience business growth that outstrips infrastructure capabilities
Platform as a Service (PaaS) fits organizations that want to:
- Develop or host new custom applications without any hassles and costs of installing hardware or software
- Free developers to focus on their application code through simpler, faster, and secure app development
- Analyze and mine data, find insights and patterns, and predict outcomes to improve forecasting, product designs, ROI, and other business decisions
- Access and use sophisticated software development kits and BI and analytics tools that are priced high
- Develop for multi-platforms, including mobile and web browsers using the same code base
- Implement agile methodologies to test and prototype new applications more quickly and gather user feedback
Are You Looking For A Cloud Service Provider?
Deployment Models
How to choose the right cloud deployment model?
There are three different cloud computing deployment models: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.
Public Cloud
Managed by third-party cloud service providers that offer compute, storage, and network resources over the internet to users
Private Cloud
Built, managed, and owned by a single organization and privately hosted in their own on-premise data centers
Hybrid Cloud
Combines public and private cloud models to provide the security and compliance capabilities commonly found in private cloud architectures
Software as a Service (SaaS) fits organizations that want to:
- Apps and services required to perform IT and business operations
- Additional resource requirements to address varying peak demands
- Foreseeable computing needs, such as communication services for a specific number of users
- Software development and test environments
Private cloud is suitable for:
- Highly regulated industries, such as banking, government, finance, and healthcare
- Handling sensitive data
- Companies that require strong control and security over their IT workloads and the underlying infrastructure
- Large enterprises that need advanced data center technologies to operate efficiently and cost-effectively
- Organizations that can afford to invest in high performance and availability technologies
Hybrid cloud is suitable for:
- Organizations catering to diverse verticals having different IT security, regulatory, and performance requirements
- Optimizing cloud investments without compromising on the value that public or private cloud technologies can deliver
- Improving security on existing cloud solutions such as SaaS offerings that must be delivered via secure private networks
- Strategically approaching cloud investments to continuously switch and tradeoff between the best cloud service delivery model available in the market
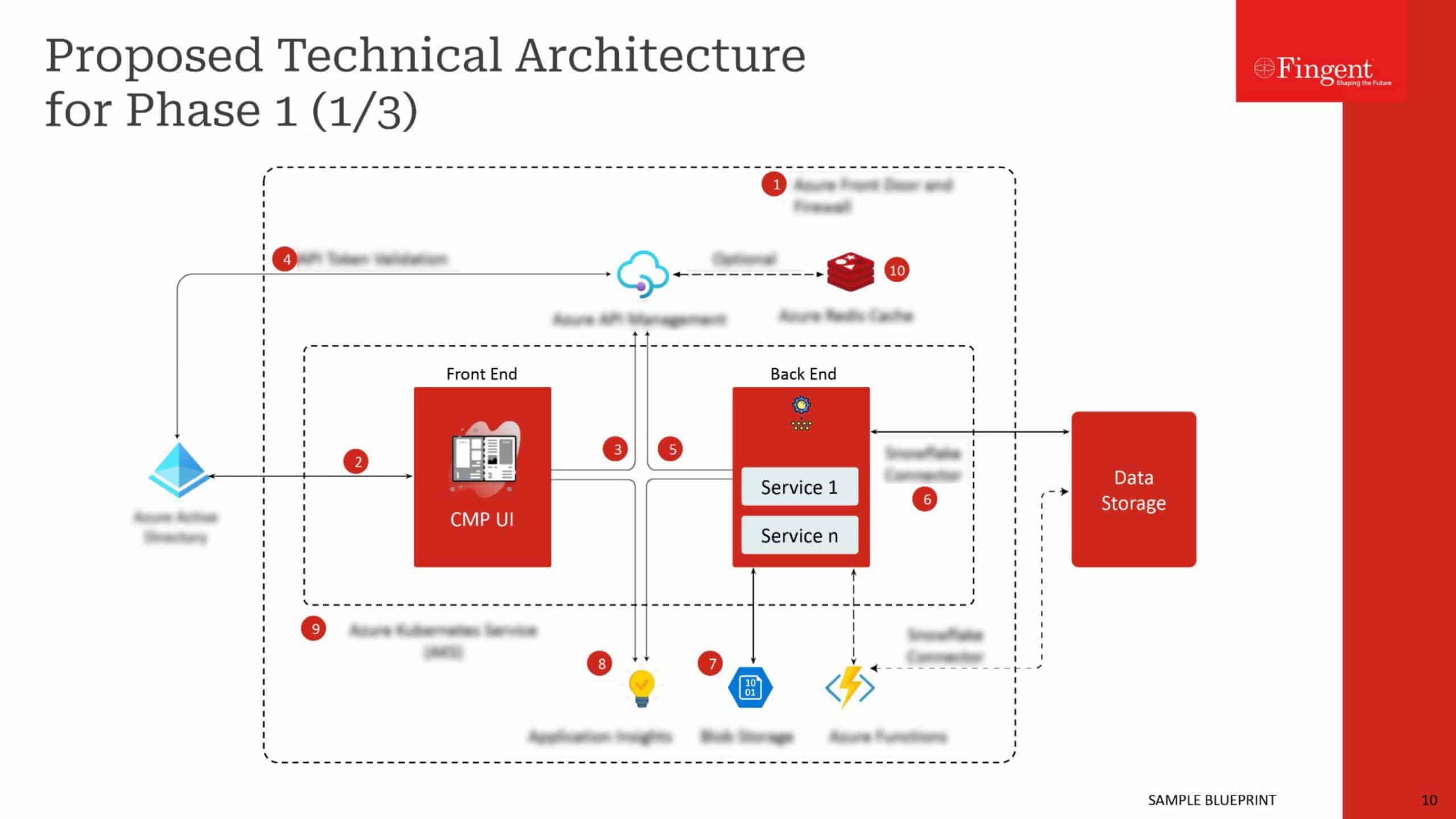
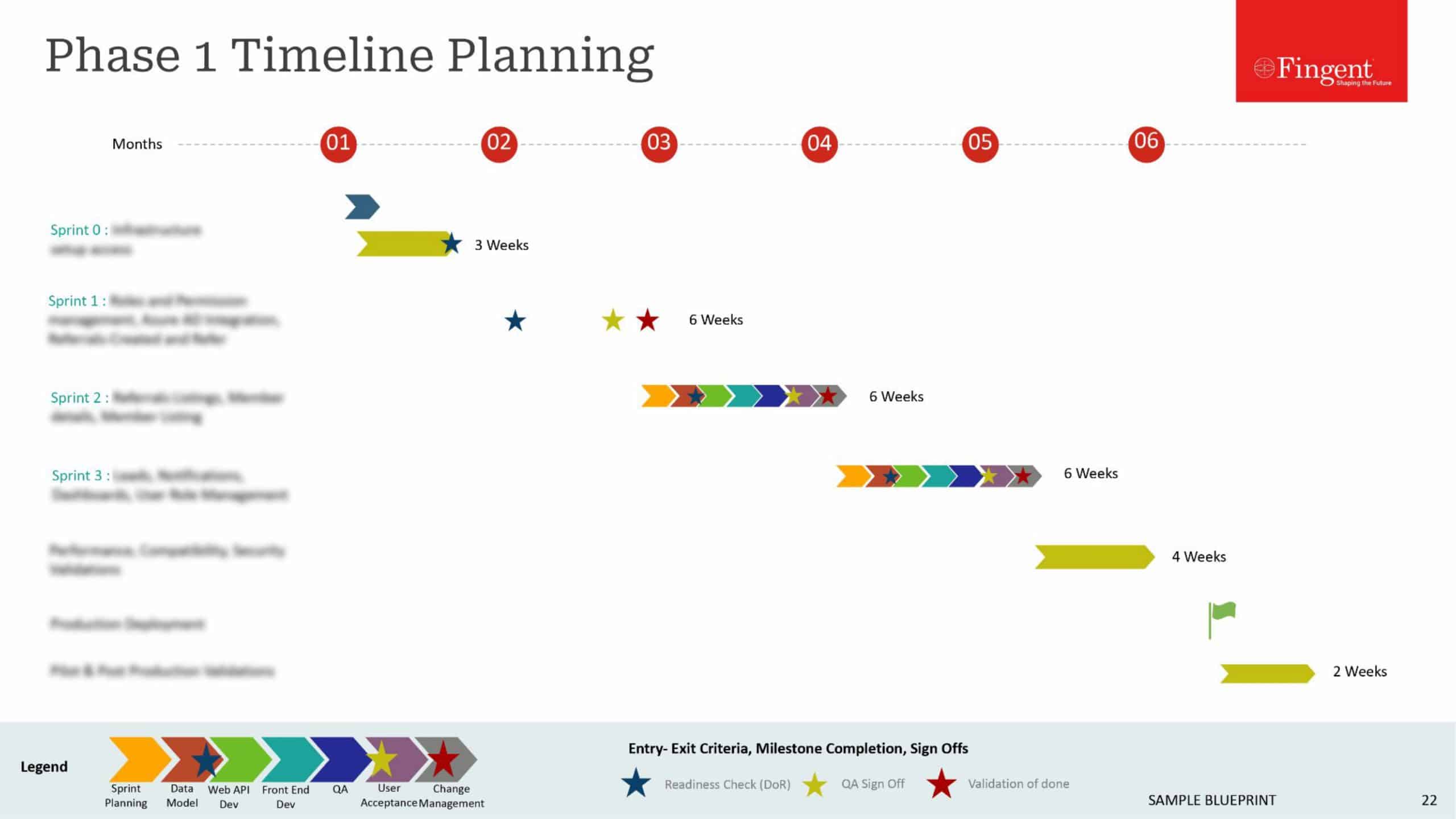
Migration Checklist
Checklist for organizations to plan cloud migration journey
Migrating existing services to the cloud as well as provisioning new workloads in the cloud require careful planning and preparation. With the right cloud migration planning, IT leaders can reduce the complexity, save time, and mitigate risks during the migration process. This checklist presents the various phases of cloud migration along with the activities to track in each stage.
#1 Workload analysis: Assess your system’s cloud readiness, complexity, application dependencies, impact of migration, hosting and resource requirements, order of apps or services to be migrated to cloud, support from your on-prem vendor during cloud migration, and restrictions to adapt to cloud, among others.
#2 Cloud migration strategy and roadmap: Choose the right migration strategy, cloud service provider, and migration tool based on your requirements.
#3 Proof of Concept test before actual migration: Running a POC before officially migrating the workloads to cloud will allow IT teams to make the essential customizations. It helps analyze the cloud environment prerequisites for migration, simulate the real-world to test the performance, and run tests to keep cloud budgets in line.
#4 Migrating workloads to the cloud: This stage involves prioritizing workloads for migration, testing new deployments thoroughly, and directing user traffic to the new cloud environment.
#5 Optimizing and fine-tuning the new cloud environment: The cloud environment can be optimized based on the organization’s operational usage patterns. Workloads can be monitored constantly to identify over-utilized and under-utilized cloud services to optimize resource utilization and reduce billing overages. The old on-prem work environment can be closed/ decommissioned after solving the issues occurring during migration.
Ready To Migrate To The Cloud?
Pros & Cons of Cloud
Benefits and risks of cloud adoption
Benefits
- Effective cross-team collaboration
- Faster service deployment
- Better cost savings and ROI
- Automatic software updates
- High availability and reliability
- Easy to scale
- Anytime, anywhere access
Risks
- Inadequate access to right expertise and resources
- Third-party hosting can minimize governance control
- Security vulnerabilities
- Portability between cloud providers
- Compliance and legal issues
- Hidden costs
- Migration complexities
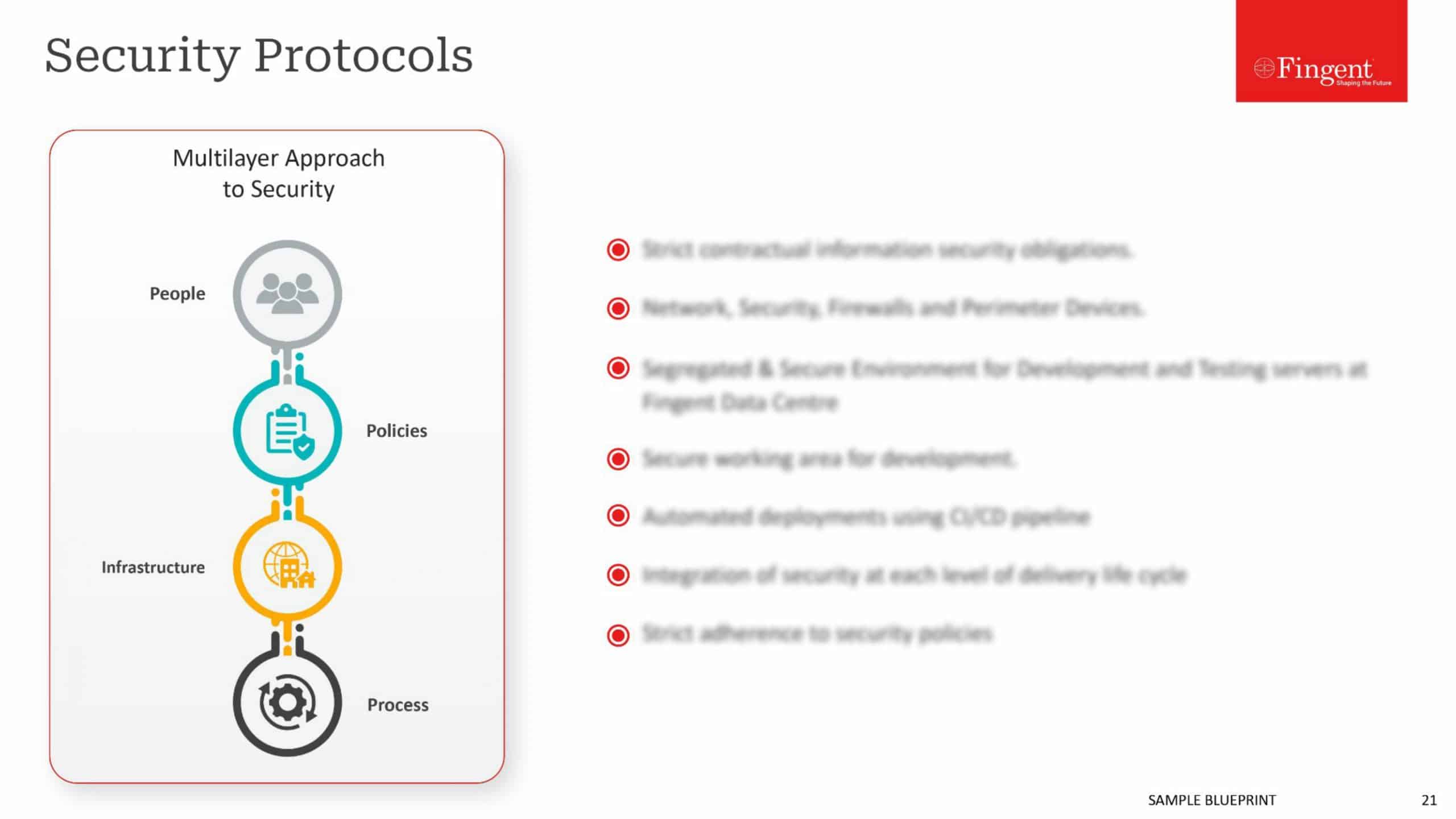
Ensuring Cloud Security
Best practices for CIOs and CTOs to ensure cloud security
- Define authentication and role based access controls, including Identity and Access Management (IAM), role and policy identification, and Active Directory (AD) integration
- Identify data protection and encryption/decryption solutions, including data lifecycle management, encryption key management, personal privacy information protection, etc.
- Validate network architecture to enforce zoning and protection mechanisms, such as VLAN segregation, security group templates, VPN connect, and least privilege access definition
- Assess the security of cloud services (PaaS) used in the environment, such as application threat modeling, web scanning tools, test data sanitization approach, etc.
- Evaluate log sources and define the method for logging and reporting with analytics, including log collection & storage architecture, tool selection, log lifecycle management, etc.
- Set up patching and update processes for enhancing infrastructure security (OS patching and hardening tools, storage hardening policies, database patching approach)
- Design and implement a continuous monitoring and improvement model for enhancing security architecture comprising periodic environments audits, security test design and approach, and evaluation of new security offerings
Cloud Costs & ROI
Factors that influence cloud costs and ROI
What drives cloud costs?
- Current infrastructure maintenance costs
- Estimated cloud infrastructure costs (compute, storage, networking, and user requirements)
- Pricing plans of cloud service providers
- Estimated cloud migration and post-migration costs
- Customization and deployment requirements/ challenges
- Third-party integrations
- Additional security measures
What drives cloud ROI?
- Returns from monetary investments
- Enterprise-wide agility
- Better alignment of IT infrastructure and management costs with the business goals
- Faster time to market
- Flexibility to scale up or down computing resources based on demand
- Automated IT management and provisioning
- Integrated business intelligence and analytics platforms
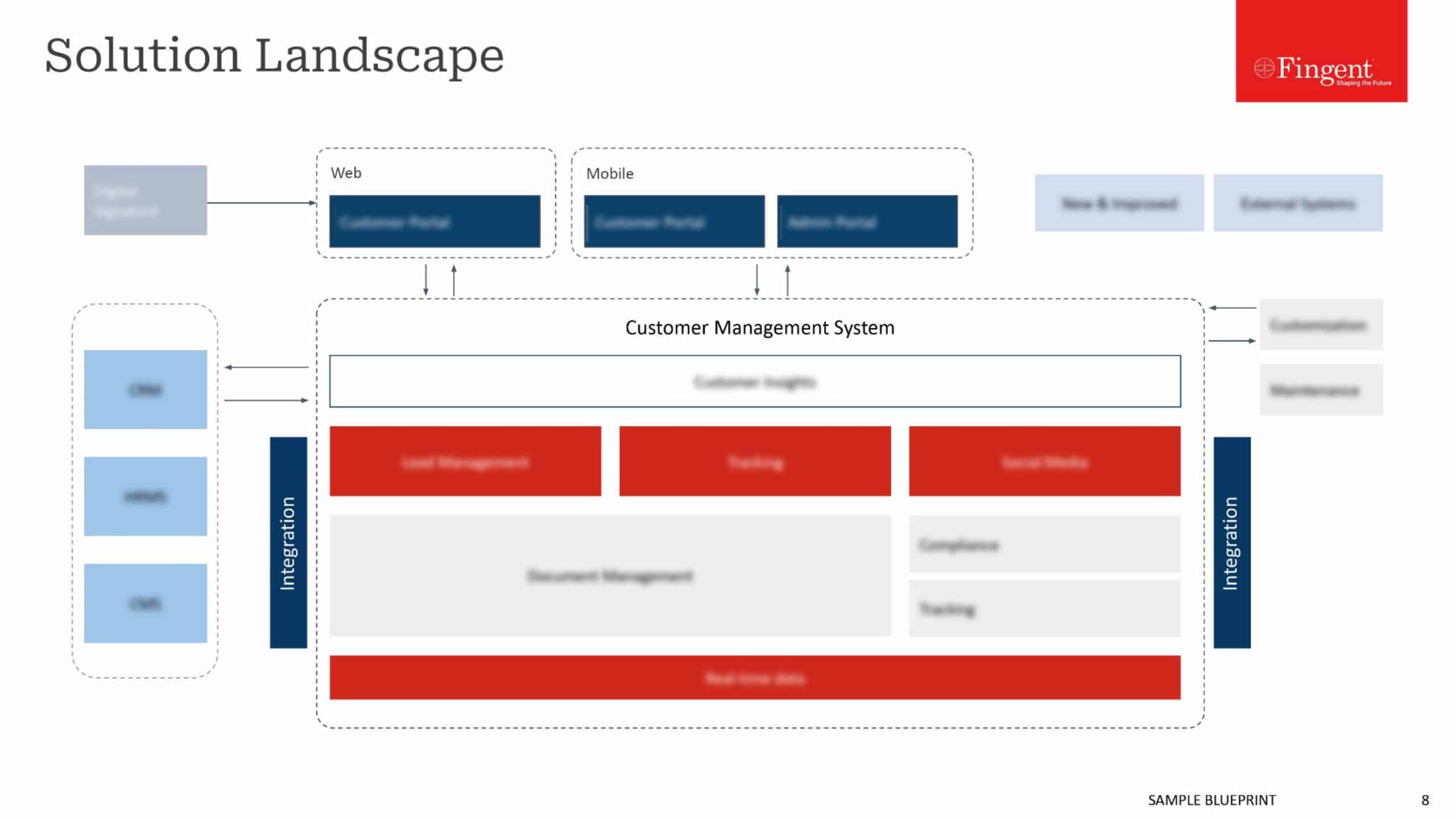
Fingent’s Approach
Cloud native development and application modernization
Fingent’s approach to cloud native development
- Service-oriented architecture: Design the application as a collection of services
- Decouple the data into separate components, so it can be stored and processed on any public or private cloud instance
- Optimize the communications between application components
- Analyze how the application components handle load traffic by testing using a model
- Use performance monitoring tools to monitor overall application performance and scaling
- Design and integrate security into the application architecture
Fingent’s approach to application modernization
- Assess the state of current IT infrastructure
- Define the future state, that is, the potential cloud infrastructure
- Assess approach viability by analyzing the computing service model, deployment model, constraints posed by the existing infrastructure, etc.
- Create a roadmap for cloud migration (refer to the migration checklist given above)
- Implement and iterate modernization steps
- Maintain and operate the new cloud application and environment
Looking For Experts To Discuss Your Cloud Requirements?
Success stories
Cloud-driven business transformation: Fingent’s success stories
1. Net lease trading platform development
A leading investment brokerage firm partnered with Fingent to reap the benefits of data-backed decision-making. We helped them create a net lease trading platform that improved the volume of commercial real estate market transactions and sales.
- Ability to add, update, and manage offers on multiple property listings
- Demonstrate property listings to buyers and investors from anywhere, anytime, using any device
- Custom property and 1031 exchange dashboards for principals, brokers, and investors
- Up-to-date insights on current market trends and comparable analytics
2. B2B ecommerce platform development
Fingent assisted Kogland, a leading B2B supplier of medical equipment and consumables, to upgrade and transform their online marketplace. The new ecommerce platform makes healthcare procurement easy and fast for Kogland.
- Standardized pricing without the involvement of middlemen
- 200% increase in traffic from targeted customers
- 50% increase in conversions
Insights
More Insights on Cloud Application Development Service
Cloud Service Models Saas, IaaS, PaaS – Choose the Right One for Your Business
Cloud computing services and models are gaining tremendous momentum, with more businesses migrating their workloads from on-premise infrastructures to cloud. The ability to use IT infrastructure, software applications, and platforms via the internet has transformed the way businesses operate today.



 US
US Insurance
Insurance