Why RPA
Robotic Process Automation For Business Transformation
What is Robotic Process Automation?
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a non-invasive and easy-to-implement software technology used for building, deploying, and managing software robots that emulate human actions interacting with digital systems and software. RPA software automates repetitive, rules-based tasks that rely on structured, digital data.
How RPA drives business transformation?
- Reduces staffing costs and enables workforce to contribute to higher-value business areas that need manual intervention
- Effectively handles tasks like data entry, error reconciliation, and rule-based decision-making
- Reduces the scope for human errors with an increased volume-handling capacity
- Automation of numerous tasks across business processes improves productivity and increases return on investments
- AI- and ML- powered customer service/ tech support chatbots with builtin software robotic scripts enable businesses to deliver a remarkable customer experience
Feasibility
What kind of business processes are a good fit for RPA?
RPA is best suited for automating:
- Consistent, rule-based, and data-driven tasks that are highly definable and occur the same way every time
- Repetitive and lower-value work, such as logging into applications and systems, moving files and folders, copying and pasting, form filling, etc.
- High-volume tasks, such as managing orders, requests, and complaints received round the clock, as software robots are able to work 24/7/365
- Back-office tasks that tend to be more transactional and repetitive
RPA is not meant for automating:
- Tasks that are constantly changing, not easy to define, non-standardized, and unstable
- Front-office tasks that require complex thinking, judgment, and decision-making skills
- Task-focused micro-workflows that include several layers of related subtasks, delegations, approvals, and reports, requiring collaboration with different departments and complex decision-making
RPA or IA
Robotic Process Automation vs. Intelligent Automation
RPA
- Automates rule-based, repetitive tasks that have no variation
- Performs routine tasks by following predefined instructions with more efficiency and less error rate
- Simple automation using software bots
- Automates non-routine tasks that require judgment and complex decision-making
- Detects and adapts to constant changes
- Handles exceptions efficiently
- Combines ML, computer vision, text analytics, and NLP
Considerations
Factors to consider when implementing RPA
- Approaching tasks with an “automation first” mindset will allow C-suite leaders to attain long term success with RPA
- Mechanisms to identify processes that are good candidates for RPA
- Segregation of business processes that can and cannot be automated by RPA (either fully or partially)
- Identification of tasks that would benefit from a blend of humans and robots working together
- Discovery of business problems that automation will solve
- Methods for evaluating the ROI of automation opportunities, and using those ROI calculations to prioritize automation projects
Have A Requirement To Discuss?
Infrastructure
Infrastructure considerations to set up RPA in business
- RPA tool licenses for development, testing, and implementation
- RPA tool support for Virtual Machines (VMs) and Cloud environments
- Compatibility of the RPA tool with your server and server versions, especially for VM servers
- Impact of security policies and software update policies on the RPA tool functionality
- Infrastructure setup and configuration of supporting tools (eg: OCR, Microsoft Office, emails) required to make RPA more functional
- Monitoring and maintenance of production environment on a regular basis
- Restrictions to access higher level environments based on organizational policies
- Allocation of access request based on Active Directory (AD) security groups
Benefits & Challenges
Benefits & challenges of RPA implementation
Benefits
- Minimal disruption to the underlying systems
- Simple, drag-and-drop UI features
- Easy onboarding of non-technical staff
- Better accuracy and compliance
- Improved focus on thoughtful and strategic decision-making
- Higher rates of customer satisfaction
Challenges
- Adaptability of workforce to changes in the way of work
- Preparing teams by investing in training programs
- Efforts to promote a culture of learning and innovation
- Changes in job roles and adapting to new roles
- Difficulty in scaling RPA program
- Regulatory updates and internal changes
Industry Applications
RPA use cases across industries and business operations
Banking and financial services: Banks use RPA solutions to automate tasks, such as customer research, account opening, credit card applications, inquiry processing, and anti-money laundering. RPA-based bots automate and streamline tedious, rule-based manual tasks like high-volume data entry.
Healthcare : Healthcare providers and hospital networks use RPA software to optimize information management, prescription management, insurance claim processing, and payroll processing, among other processes.
Insurance : Insurance companies use RPA for automating transactional operations, claims processing, premium payments and reconciliation, post-sale services, regulatory compliance, policy management, and underwriting tasks.
Retail : Modern retailers use RPA to improve back office operations and customer experience. Popular applications include customer relationship management, warehouse and order management, sales order entries, invoice processing, customer feedback processing, and fraud detection.
Manufacturing : RPA is widely used in manufacturing for automating routine industrial tasks, IT issues, repetitive HR tasks, bills of material (BOM), purchase orders, purchase requisitions, invoice processing and also for improving supply efficiency and accuracy, compliance management, and customer self-service and engagement, among other processes.
IT Enterprises : IT companies and organizational departments use RPA to automate routine tasks, such as password management, notifications management, ticketing workflows, roll out and installation of software updates, etc.
Cost & ROI
Factors influencing RPA implementation costs and ROI
RPA Costs
- Cost of the RPA solution, including licensing, subscription, maintenance, etc.
- Additional infrastructure costs, including hardware, software, and networking
- Development and maintenance costs
- Extra costs related to infrastructure set up, customization, and bot configuration
- Line of business and the impact of changes across departments
RPA ROI
- Returns from monetary investments
- Cost reduction
- Moving employees to higher-value work
- Reduction in manual errors
- Productivity and quality improvement
- Innovation acceleration
- Business continuity, agility, and analytics enhancement
Approach
Fingent’s Approach to Robotic Process Automation
The growing interest in Robotic Process Automation points to the increasing deployments reaching enterprise scale and automation of tasks across various routine operations.
Fingent follows a robust and proven methodology for RPA software development and support.
#1 Evaluate: Assess the existing processes, organizational fit, and readiness for RPA.
#2 Identify: Make a strong case for automation by identifying the best process candidates to automate first.
#3 Define Requirements: Define the scope, applicability, and impact of potential process automation. Understand and finalize the key requirements.
#4 Proof of Concept: Pilot selected process and measure the performance of pilot against objectives
#5 Design: Define target state for business, performance model, level of automation needed, and process design
#6 Develop: Develop target solutions, configure robotics software, and end state design
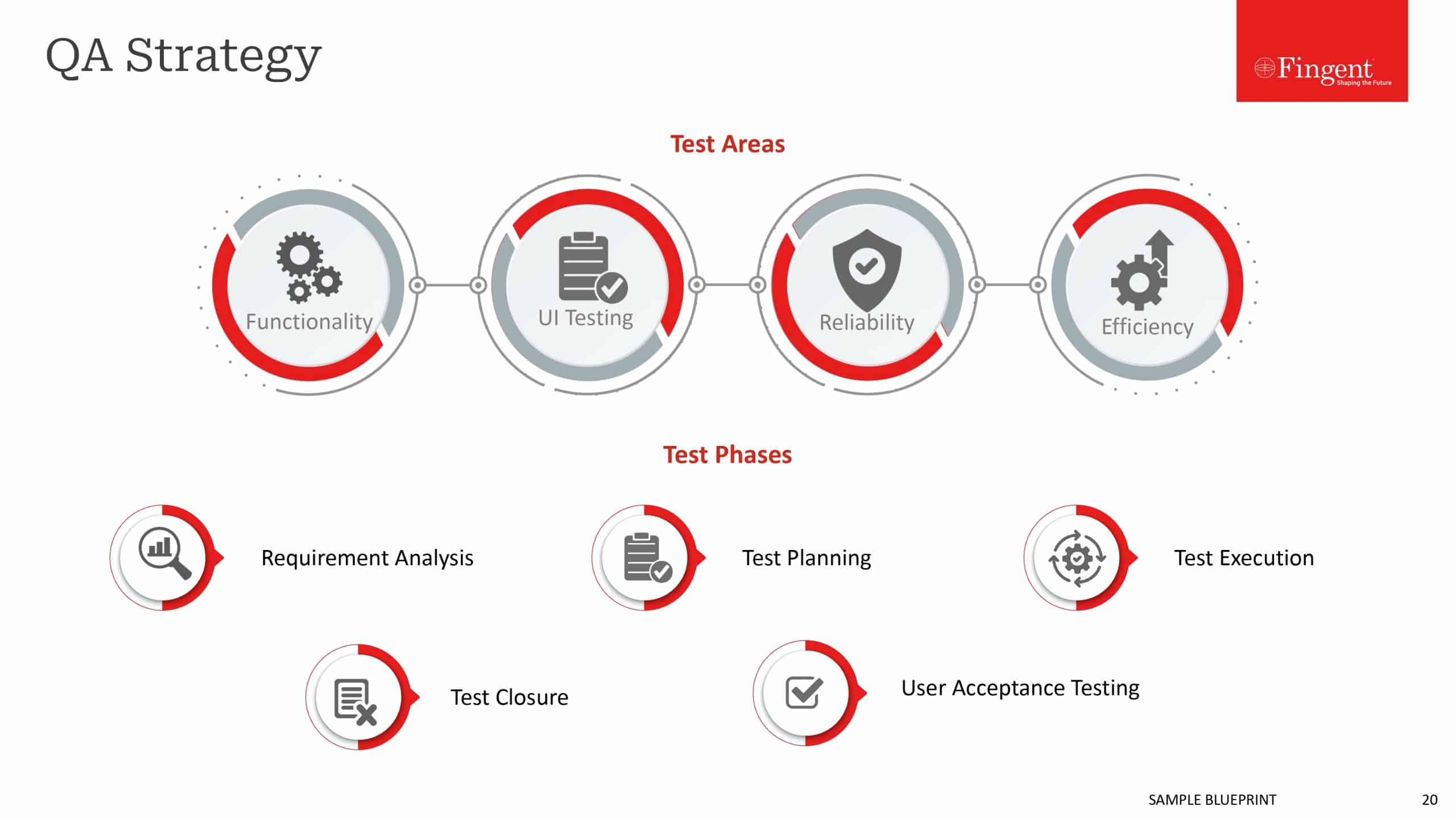
#7 Test: Test the performance of the robotics software and make improvements as needed, fix bugs, and conduct QA
#8 Support: Decide the ongoing support model for automation, change management, and periodic reviews to ensure continuous improvement and business innovation
Free consultations
Ideation

Strategy
Design

Development

Testing
Maintenance
Unsure About How To Get Started With RPA?
Insights
More Insights on Robotic Process Automation

Deploying RPA for Finance, Healthcare & IT Operations
Digital transformation has become indispensable, more so now than ever before. When COVID-19 struck, governments swung into action and issued orders that restricted in-person business operations and encouraged people to work from home.


 US
US Insurance
Insurance